10 Random Questions
While delivering nitrous oxide 1.5 L/min, oxygen 1.5 L/min, and halothane 1%, a leak in the oxygen flowmeter will most likely be detected by the
- (A) low airway pressure alarm
- (B) "fail-safe" system
- (C) oxygen analyzer on the expiratory limb
- (D) oxygen flowmeter reading
- (E) mass spectrometric analysis of gases
A 75-kg, 45-year-old patient with quadriplegia at the level of C6 is scheduled for elective cholecystectomy. Pulmonary function tests show an FVC of 2.4 L and an FEV, of 1.2 L. Which of the following is the most appropriate conclusion based on these findings?
- (A) Intercostal muscle function is normal
- (B) SpO, will be 80% or less while breathing room air
- (C) Total lung capacity is normal
- (D) The patient has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- (E) These findings are expected in this patient
Each of the following factors may lead to erroneous readings using pulse oximetry EXCEPT
- (A) electrocautery
- (B) high cardiac output states
- (C) infrared lights near the sensor
- (D) intravenous dyes
- (E) severe hemodilution
Which of the following combinations of hemoglobin, blood gases, and cardiac output provides the greatest delivery of oxygen to tissue? (Hb, PaO2, SaO2, CO)
- (A) 7.0 85 95 7.0
- (B) 8.0 290 100 8.0
- (C) 9.9 61 90 9.8
- (D) 12.0 140 100 4.5
- (E) 16.0 40 75 5.8
Which of the lines shown in the graph illustrates the relationship of hematocrit and oxygen transport?
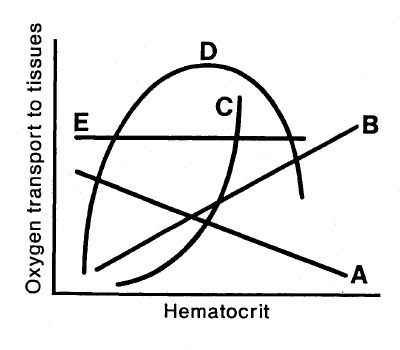
- (A) Line A
- (B) Line B
- (C) Line C
- (D) Line D
- (E) Line E
During liver transplantation, venovenous bypass from the femoral and portal veins to the axillary vein during cross-clamping of the inferior vena cava
- (A) decreases urine output
- (B) prevents hypothermia
- (C) prevents metabolic acidosis
- (D) requires heparinization
- (E) supports cardiac output
Delirium produced by high doses of atropine can be reversed by intravenous injection of
- (A) diphenhydramine
- (B) flumazenil
- (C) naloxone
- (D) neostigmine
- (E) physostigmine
A patient has severe hypotension, bronchospasm, and edema of the upper airway after injection of radiocontrast medium during cerebral angiography. The most appropriate immediate treatment is administration of
- (A) diphenhydramine
- (B) epinephrine
- (C) methylprednisolone
- (D) phenylephrine
- (E) ranitidine
A multi-orifices right heart catheter is being positioned by EKG control prior to sitting craniotomy. The EKG tracing is obtained between the distal tip of the catheter and the right arm lead. The most appropriate next step is to

- (A) leave the catheter in place
- (B) advance the catheter 2 to 3 cm
- (C) withdraw the catheter 2 to 3 cm
- (D) remove the catheter completely
- (E) change polarity of the EKG
Compared with adults, caudal anesthesia in children is associated with
- (A) higher risk for subarachnoid puncture
- (B) more severe hypotension
- (C) more rapid onset of sensory block
- (D) smaller volume of anesthetic per kilogram of body weight
- (E) toxic effects at lower serum levels of bupivacaine