10 Random Questions
A 20-year-old man involved in a motor vehicle accident is brought to the operating room for irrigation and debridement of open fractures of the femur and humerus. Cyanosis, decreased breath sounds on the left, increased peak airway pressure, and hypotension are noted after intubation of the trachea. The most likely cause is
- (A) aspiration
- (B) fat embolus
- (C) intubation of the right mainstem bronchus
- (D) tension pneumothorax
- (E) unilateral bronchospasm
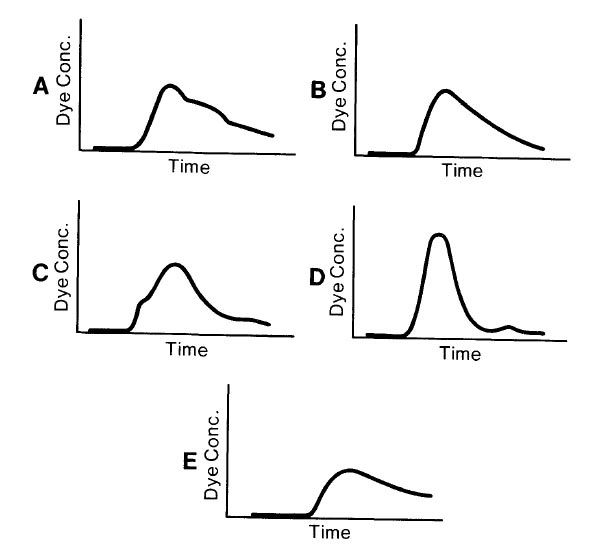
Which of the following time concentration curves would be expected in arterial blood following intravenous injection of indocyanine green dye in a 3-year-old child with a small ventricular septal defect?
A 48-year-old woman with von Willebrand's disease is scheduled for a hysterectomy. The most appropriate initial preoperative therapy to decrease bleeding is administration of
- (A) cryoprecipitate
- (B) desmopressin (DDAVP)
- (C) fresh frozen plasma
- (D) platelets
- (E) vitamin K
Each of the following is a characteristic of prostaglandin E1 (alprostadil) pharmacology in an infant EXCEPT:
- (A) It is effective in the treatment of large left-to-right shunts
- (B) It is a cause of apnea
- (C) It is a potent vasodilator
- (D) It prevents closure of the ductus arteriosus
- (E) It is metabolized rapidly
As part of a preoperative evaluation, a patient had a thallium scan showing a 'cold spot' over the left ventricle that occurs with moderate exercise and disappears at rest. This most likely indicates
- (A) moderate-sized aneurysm of the left ventricle
- (B) acute myocardial ischemia
- (C) recent myocardial infarction
- (D) old myocardial infarction
- (E) Prinzmetal's variant angina
In a 45-year-old patient with severe mitral regurgitation, which of the following is the most important hemodynamic condition to avoid during induction of anesthesia?
- (A) Decreased heart rate to less than 60 bpm
- (B) Increased heart rate to greater than 90 bpm
- (C) Increased preload
- (D) Increased afterload
- (E) Enhanced myocardial contractility
Awakening after a single dose of thiopental is caused by redistribution from the brain primarily to which of the following sites?
- (A) Fat
- (B) Heart
- (C) Liver
- (D) Lung
- (E) Skeletal muscle
A 50-year-old patient is undergoing craniotomy for clipping of a cerebral aneurysm with isoflurane, nitrous oxide, and fentanyl anesthesia. At the time of aneurysm exposure, the EEG shows burst suppression. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Cerebral ischemia
- (B) Cerebral vasospasm
- (C) Fentanyl effect
- (D) Isoflurane effect
- (E) Petit mal seizure activity
A 95-kg, 65-year-old woman receives sevoflurane and pancuronium during a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Three minutes after administration of neostigmine 5 mg and atropine 1.2 mg, the twitch height returns to normal. Spontaneous tidal volume is 500 ml when the endotracheal tube is removed. In the PACU she reports dyspnea and appears distressed. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the respiratory distress?
- (A) Atelectasis
- (B) Cholinergic crisis
- (C) Pain
- (D) Residual enflurane
- (E) Residual muscle paralysis
Which of the following statements concerning the pharmacokinetics of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants is true?
- (A) Drugs with a longer duration of action depend on the liver for excretion
- (B) Drugs with a shorter duration of action depend primarily on redistribution for recovery
- (C) Onset of action is independent of dose
- (D) Recovery rate parallels the decrease in plasma relaxant concentration
- (E) The shorter the duration of action, the faster the onset