284 questions match your search.
A 20-year-old woman with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus is scheduled for urgent drainage of an abdominal abscess. She received an initial dose of regular insulin 10 units followed by regular insulin 5 units/hr for the past five hours. Laboratory studies show serum sodium concentration 128 mEq/L, potassium 5.4 mEq/L, chloride 80 mEq/L, and glucose 750 mg/dl. The most appropriate perioperative management is
- (A) addition of subcutaneous NPH insulin
- (B) administration of sodium bicarbonate to correct metabolic acidosis
- (C) administration of normal saline solution to correct the presumed hypovolemia
- (D) administration of furosemide to correct hyponatremia
- (E) infusion of 5% dextrose in 0.2% saline solution to prevent hypoglycemia
A 25-year-old man requires exploratory laparotomy following a motor vehicle accident. He is acutely intoxicated with alcohol. Which of the following is the most likely result of the alcohol ingestion?
- (A) Hyperdynamic circulation
- (B) Hyperglycemia
- (C) Hyperthermia
- (D) Increased respiratory depression from opioids
- (E) Increased sensitivity to neuromuscular blocking drugs
During enflurane anesthesia for colectomy in a 75-year-old man with sepsis, urine output decreases to 10 ml/hr. Heart rate is 120 bpm, blood pressure is 100/50 mmHg, central venous pressure is 10 mmHg, and pulmonary artery occlusion pressure is 15 mmHg. The most appropriate management at this time is to
- (A) measure cardiac output
- (B) increase fluid administration
- (C) infuse dopamine
- (D) administer propranolol
- (E) switch from enflurane to isoflurane
A 63-year-old man with a history of congestive heart failure and left ventricular dilation is scheduled for carotid endarterectomy. During carotid cross-clamping, the surgeon requests that systolic blood pressure be increased from 100 to 160 mmHg. Compared with an identical patient with normal left ventricular size, what is the effect of this change in blood pressure on this patient's myocardial oxygen consumption?
- (A) Equal decrease
- (B) Greater decrease
- (C) Lesser increase
- (D) Equal increase
- (E) Greater increase
During a reoperative total hip arthroplasty requiring transfusion of 8 units of packed red blood cells, blood begins to ooze from the operative field and intravenous catheter sites. Urine is pink. The most likely cause is
- (A) citrate intoxication
- (B) factor V and VIII deficiencies
- (C) rhabdomyolysis
- (D) thrombocytopenia
- (E) transfusion reaction
During cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) in an adult, external chest compression is being performed at the rate of 90/min with 2 inches of sternal depression and a compression-relaxation ratio of 20:80. The most appropriate action is to
- (A) decrease the rate of compression
- (B) increase the duration of compression
- (C) increase the duration of relaxation
- (D) increase the depth of sternal depression
- (E) continue the original pattern of CPR
As part of a preoperative evaluation, a patient had a thallium scan showing a 'cold spot' over the left ventricle that occurs with moderate exercise and disappears at rest. This most likely indicates
- (A) moderate-sized aneurysm of the left ventricle
- (B) acute myocardial ischemia
- (C) recent myocardial infarction
- (D) old myocardial infarction
- (E) Prinzmetal's variant angina
You are called to anesthetize a patient for an emergency pericardial window for a large pericardial effusion. Which of the following drugs is most appropriate for initiation of anesthesia?
- (A) Alfentanil
- (B) Ketamine
- (C) Midazolam
- (D) Propofol
- (E) Thiopental
Which of the following statements concerning neuroleptic malignant syndrome is true?
- (A) It does not respond to dantrolene therapy
- (B) It is inherited as an autosomal trait
- (C) It is not triggered by succinylcholine
- (D) It occurs after long-term use of L-dopa
- (E) The halothane-caffeine contracture test is negative in susceptible patients
A 50-year-old man who takes aspirin and nifedipine is scheduled for thoracotomy with one-lung ventilation. Which of the following is associated with the greatest risk for intraoperative hypoxemia?
- (A) Preoperative withdrawal of nifedipine therapy
- (B) Intraoperative mild respiratory acidosis
- (C) Intraoperative administration of isoflurane
- (D) Intraoperative administration of nitroglycerin
- (E) Intraoperative thoracic epidural morphine
Which of the following statements concerning neuroleptic malignant syndrome is true?
- (A) It does not respond to dantrolene therapy
- (B) It is inherited as an autosomal trait
- (C) It is not triggered by succinylcholine
- (D) It occurs after long-term use of L-dopa
- (E) The halothane-caffeine contracture test is negative in susceptible patients
A 15-year-old previously healthy boy is scheduled for a celiotomy to relieve an acute intestinal obstruction. A rapid sequence induction is used. Anesthesia is maintained with a balanced technique including nitrous oxide and oxygen (5L:2L), meperidine, and pancuronium. Because of abdominal distention and the high pressure required for inflation of the lungs, a nasogastric tube is inserted. The abdomen remains distended, but compliance improves dramatically. At this time the patient is cyanotic, PaO2 is 48 mmHg, PaCO2 is 52 mmHg, and pH is 7.29. Nitrous oxide is discontinued. The most important therapeutic measure is to
- (A) remove the nasogastric tube
- (B) insert a chest tube on the right side
- (C) withdraw the endotracheal tube 1 cm
- (D) deflate the cuff on the endotracheal tube
- (E) replace the endotracheal tube with one of larger internal diameter
When methylmethacrylate is inserted into the femur, each of the following may occur EXCEPT
- (A) monomer metabolic breakdown
- (B) vasodilation
- (C) hypercarbia
- (D) hypoxia
- (E) increased intramedullary pressure
A 45-year-old man with chronic liver failure is scheduled for liver transplantation. Which of the following preoperative findings is most likely?
- (A) Hypoxemia
- (B) Increased platelet count
- (C) Increased systemic vascular resistance
- (D) Increased serum factor VIII concentration
- (E) Metabolic alkalosis
Initiation of positive pressure mechanical ventilation is LEAST likely to decrease cardiac output in patients with which of the following conditions?
- (A) Abdominal distention with decreased lung volume
- (B) Acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema
- (C) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- (D) Flail chest following an automobile accident
- (E) 20% Right pneumothorax
Which of the following statements concerning awareness (recall) during opioid anesthesia is true?
- (A) It is usually not associated with pain
- (B) It correlates well with intact auditory evoked responses
- (C) It is prevented if the dose of opioid blocks the hemodynamic response to stimuli
- (D) It is prevented if the dose of opioid is adequate to prevent movement without muscle relaxants
- (E) It is predicted by a specific EEG pattern
A 70-year-old man who has just undergone an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair under halothane anesthesia develops hypertension, dyspnea, and cyanosis shortly after awakening in the recovery room. Administration of furosemide 20 mg intravenously improves the cyanosis within 10 minutes. This immediate effect of furosemide is best explained by
- (A) inotropic effect from electrolyte shifts
- (B) decreased preload through diuresis
- (C) increased peripheral venous capacitance
- (D) decreased pulmonary vascular resistance
- (E) increased coronary blood flow
Each of the following statements about pheochromocytoma is true EXCEPT:
- (A) Preoperative administration of alpha-adrenergic inhibitors will usually reverse EKG changes due to catecholamine myocarditis
- (B) Preoperative administration of alpha-adrenergic inhibitors decreases operative mortality
- (C) Beta-adrenergic inhibitors should be administered preoperatively only in conjunction with alpha-adrenergic inhibitors
- (D) Vasopressor therapy may be necessary postoperatively for treatment of hypotension
- (E) Nasal congestion is a sign of inadequate alpha-adrenergic block
The mortality rate of patients given drug A is 12% (8 of 66) and the mortality rate of patients given drug B is 15% (10 of 66). Which of the following tests is most appropriate to compare these mortality rates?
- (A) t-Test for paired data
- (B) t-Test for unpaired data
- (C) Wilcoxon rank test
- (D) Chi-square test
- (E) Analysis of covariance
A 75-year-old, 60-kg man with moderately disabling heart failure secondary to ischemic heart disease is undergoing a transurethral prostatic resection under halothane-nitrous oxide anesthesia. Resection time is 30 minutes, and fluid replacement has been lactated Ringer's solution 500 mL. Although heart rate is unchanged, the arterial pressure monitor used because of his cardiac condition has changed from A to B over the last 15 minutes. The most appropriate management is to
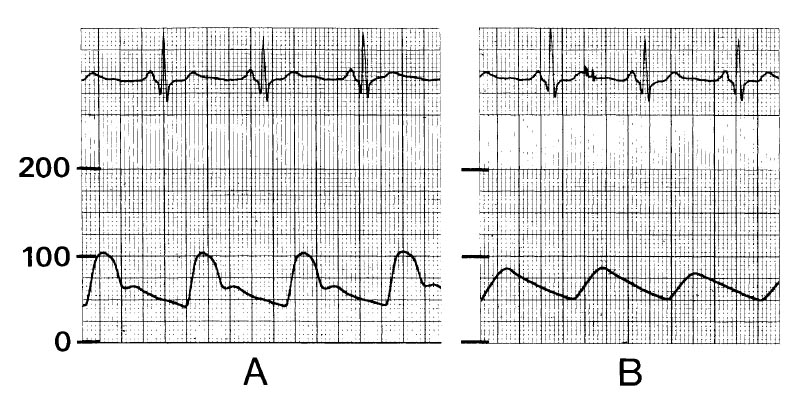
- (A) discontinue halothane
- (B) adminster ephedrine 10 mg intravenously
- (C) administer digoxin one half of his daily dose intravenously
- (D) administer sodium chloride 100 mL of 3%
- (E) do none of the above
A patient is undergoing thoracotomy in the lateral position. Five minutes after initiation of one-lung ventilation using a double-lumen tube and 100% oxygen, SpO2 decreases from 100% to 65%. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?
- (A) Adding continuous positive airway pressure to the nondependent lung
- (B) Adding positive end-expiratory pressure to the dependent lung
- (C) Increasing the tidal volume to the dependent lung
- (D) Resuming two-lung ventilation
- (E) Verifying the position of the double-lumen tube
A 26-year-old man who sustained multiple trauma undergoes open reduction and internal fixation of bilateral tibial-fibular fractures during anesthesia with isoflurane. nitrous oxide, and oxygen with positive pressure ventilation. During the procedure, the patient has sudden onset of hypotension, jugular venous distention, deviation of the trachea to the right, and decreased ventilatory compliance. Isoflurane is discontinued and 100% oxygen is administered. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- (A) Chest x-ray
- (B) Blood tranfusion
- (C) Subxiphoid pericardiocentesis
- (D) Fiberoptic bronchoscopy
- (E) Left chest needle thoracostomy
A 60-kg, 70-year-old man requires open reduction and internal fixation of an intertrochanteric fracture sustained 24 hours ago. Serum creatinine concentration is 1 mg/dl and blood urea nitrogen concentration is 40 mg/dl. The most likely cause of these findings is
- (A) acute tubular necrosis
- (B) chronic renal insufficiency
- (C) dehydration
- (D) obstruction of the bladder outlet
- (E) recent gastrointestinal hemorrhage
A patient with uremia is scheduled for emergency surgery. Bleeding time is 18 minutes. The most appropriate initial treatment is
- (A) cryoprecipitate
- (B) desmopressin
- (C) fresh frozen plasma
- (D) platelets
- (E) vitamin K
Which of the following is the most reliable indicator of adequate reversal of neuromuscular block?
- (A) Inspiratory force equal to -30 cmH20
- (B) Sustained head lift for 5 seconds
- (C) Train-of-four ratio of 0.7
- (D) Twitch height at 100% of control
- (E) Vital capacity of 15 ml/kg
A 70-kg man with ischemic heart disease is undergoing abdominal aortic aneurysm resection. At the time of infrarenal cross-clamping, 0.2-mV ST-segment depression appears on lead V5 of the ECG. Hemodynamic changes occurring at the same time are shown below. Systemic blood pressure 90/50 --> 150/90; Heart rate 80 --> 95; PAp 20/10 --> 45/24; Mean pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (mmHg) 10 --> 23; Cardiac output (L/min) 4.5 --> 3.2. Ischemia would be decreased by restoring the pre-clamp level of each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) blood pressure
- (B) heart rate
- (C) pulmonary artery pressure
- (D) pulmonary artery occlusion pressure
- (E) cardiac output
Five minutes after initiating one-lung ventilation using a double-lumen endobronchial tube, a 70-year-old patient has a decrease in Sp02 from 99% to 90%. Tidal volume and respiratory rate are unchanged. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy verifies appropriate positioning of the tube. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the desaturation?
- (A) Blood flow to the nondependent lung
- (B) Failure of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in the dependent lung
- (C) Inadequate filling of the bronchial cuff
- (D) Inadequate minute ventilation
- (E) Surgical manipulation of the nondependent lung
Preoperative administration of an alpha-adrenergic blocker for 10 days to patients with pheochromocytoma will decrease
- (A) episodic tachycardia
- (B) hyperglycemia
- (C) hypovolemia
- (D) nasal stuffiness
- (E) postural hypotension
An obese, 70-year-old woman with a long history of tobacco abuse is awake and semirecumbent after uneventful anesthesia with isoflurane for a ventral hernia repair. During the first hour in the recovery room while breathing 50% oxygen by face mask, her arterial oxygen saturation decreases to 90% while other vital signs remain satisfactory. Which of the following is most likely to be effective in the management of this situation?
- (A) Intravenous doxapram
- (B) Racemic epinephrine by inhalation
- (C) Continuous positive airway pressure by mask
- (D) Reintubation of the trachea
- (E) Coughing
Which of the following cardiovascular abnormalities is LEAST likely to be present in a patient with end-stage alcoholic cirrhosis?
- (A) Decreased myocardial contractility
- (B) High cardiac index
- (C) High mixed venous oxygen saturation
- (D) Increased peripheral vascular resistance
- (E) Low blood viscosity
The acute onset of hypotension without a decrease in mixed venous oxygen saturation is most likely associated with the onset of
- (A) hemorrhage
- (B) myocardial infarction
- (C) pulmonary edema
- (D) pulmonary embolus
- (E) sepsis
Each of the following statements concerning the activated clotting time (ACT) is true EXCEPT:
- (A) The ACT is more sensitive than the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) to blood heparin concentration
- (B) The ACT is prolonged if the specimen is not warmed during the assay
- (C) The ACT should be greater than 300 sec before initiating cardiopulmonary bypass
- (D) Hypofibrinogenemia may prolong the ACT after cardiopulmonary bypass
- (E) Whole blood is used for measurement of the ACT
Which of the following statements regarding carbon monoxide poisoning is true?
- (A) Breathing 100% oxygen at 1 atmosphere reduces the carboxyhemoglobin half-life
- (B) Effective treatment includes administration of methylene blue
- (C) It is commonly associated with respiratory acidosis
- (D) It is incompatible with a normal Sp02 while breathing room air
- (E) The oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve is shifted to the right
A 55-year-old man who is scheduled to undergo carotid endarterectomy (CEA) has a persistent myocardial filling defect at three hours on a dipyridamole-thallium scan. Which of the following statements is correct?
- (A) Coronary autoregulation is effective in this segment
- (B) Coronary revascularization should precede CEA
- (C) Isoflurane is contraindicated
- (D) Myocardial infarction is impending
- (E) There is a segment of nonviable myocardium
Which of the following is the most sensitive indicator of impending renal failure following trauma?
- (A) Central venous pressure
- (B) Creatinine clearance
- (C) Fractional excretion of sodium
- (D) Hourly urine output
- (E) Urine osmolality
The EKG rhythm shown developed during cholecystectomy in a 62-year-old man who had a myocardial infarction and is taking atenolol. The drug of choice for treating this arrhythmia is
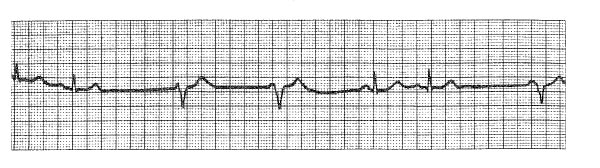
- (A) atropine
- (B) bretylium
- (C) isoproterenol
- (D) lidocaine
- (E) procainamide
Compared with a normal child, which of the following is expected during inhalation induction in a child with a 2:1 left-to-right intracardiac shunt?
- (A) Decreased rate of rise of alveolar anesthetic tension
- (B) Decreased anesthetic concentration in pulmonary artery blood
- (C) Decreased cerebral blood flow
- (D) Increased anesthetic concentration in vena cava blood
- (E) No difference in time for anesthetic induction
A 65-year-old man with essential hypertension well controlled around 140/90 mmHg with hydrochlorothiazide is scheduled for right colectomy for carcinoma. Preoperative EKG and all laboratory values are normal except for a hematocrit of 29% and serum potassium level of 3.2 mEq/L. Central venous pressure (CVP) measured from an internal jugular catheter inserted before induction of anesthesia is 7 mmHg. Ten minutes after induction with thiopental 200 mg followed by enflurane 3% in nitrous oxide and oxygen (50% each), blood pressure decreases suddenly from 110/70 to 80/50 mmHg with heart rate unchanged at 78 bpm. CVP is now 20 mmHg and the EKG demonstrates a midjunctional rhythm. After discontinuing the enflurane, the most appropriate action would be to
- (A) administer furosemide 20 mg intravenously
- (B) verify proper placement of the CVP catheter
- (C) administer atropine 0.4 mg intravenously
- (D) administer packed erythrocytes 1 unit
- (E) administer potassium 20 mEq in 250 ml of intravenous fluid over 15 minutes
A 65-year-old man has a history of alcohol abuse. Which of the following preoperative serum concentrations would provide the best assessment of synthetic hepatic function?
- (A) Albumin
- (B) Alkaline phosphatase
- (C) Bilirubin
- (D) Globulin
- (E) Transaminases
Which of the following is most likely in a 30-year-old patient with untreated hypothyroidism?
- (A) Cardiac arrhythmias with ketamine administration
- (B) Decreased ventilatory response to hypoxia
- (C) Hypoglycemia
- (D) Increased MAC of inhalational anesthetics
- (E) Peripheral vasodilatation
The cardiovascular effects of an inhalational anesthetic are evaluated in 10 normal volunteers in the awake resting state and after 15 minutes of constant inspired concentration. Results were analyzed by t-test for paired data and are presented below as mean +/- standard deviation. Based on these data, which of the following conclusions is most valid?
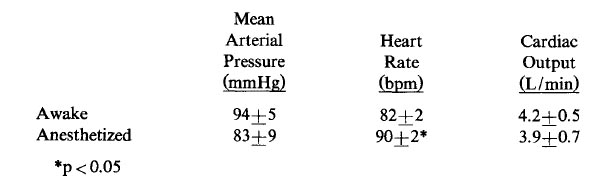
- (A) A decrease in cardiac output would have been evident if more subjects were included in the study
- (B) The anesthetic decreases mean arterial pressure
- (C) The anesthetic does not cause cardiac depression
- (D) The anesthetic is unsafe for patients with coronary after disease
- (E) There is a 95% to 100% chance that the anesthetic increases heart rate
A 72-year-old man has massive venous hemorrhage during a radical prostatectomy. Blood pressure decreases from 110/60 to 75/30 mmHg and central venous pressure decreases from 12 to 4 mmHg. PetC02 decreases from 34 to 24 mmHg during constant minute ventilation. The most appropriate next step should be to
- (A) apply positive end-expiratory pressure to the breathing circuit
- (B) attempt to aspirate air from the central venous catheter
- (C) expand intravascular volume
- (D) place the patient in the Trendelenburg position
- (E) turn the patient to the left lateral decubitus position
A 78-year-old man who is scheduled for an inguinal hernia repair has a preoperative ECG showing left bundle branch block. He has had no symptoms of cardiovascular disease. This ECG finding most likely indicates
- (A) cardiac disease
- (B) the need for spinal anesthesia
- (C) an electrolyte disturbance
- (D) the need for insertion of a temporary pacemaker
- (E) a normal finding in a patient of this age
A 64-year-old, 87-kg woman in good general health is undergoing a right knee arthroplasty while in the supine position with general anesthesia consisting of enflurane 2% and nitrous oxide 50% in oxygen. She is breathing spontaneously through a 7-mm endotracheal tube. During the first 30 minutes of the procedure, the arterial oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximetry decreases from 98% to 92%. The most likely cause of the desaturation is
- (A) decreased functional residual capacity
- (B) diffusion hypoxia
- (C) hypercarbia
- (D) increased airway resistance produced by the endotracheal tube
- (E) inhibition of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
Reduction of fire hazards during laser surgery of the airway is best accomplished by use of
- (A) continuous mode laser emissions
- (B) a nitrous oxide/opioid/relaxant anesthetic technique
- (C) a polyvinylchloride endotracheal tube and cuff
- (D) topical lidocaine
- (E) saline-filled sponges over exposed tissues
A patient has severe hypotension, bronchospasm, and edema of the upper airway after injection of radiocontrast medium during cerebral angiography. The most appropriate immediate treatment is administration of
- (A) diphenhydramine
- (B) epinephrine
- (C) methylprednisolone
- (D) phenylephrine
- (E) ranitidine
A 70-kg, 77-year-old man Is undergoing left nephrectomy with nitrous oxide, oxygen, fentanyl, and midazolam anesthesia. He has a 90 pack-year history of cigarette smoking and has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. One hour after incision, expiratory wheezing occurs and peak Inspiratory pressure increases from 35 to 65 cmH20; end-tidal PCO2 is unchanged, but SpO2 decreases from 97% to 88%. The most likely cause is
- (A) endobronchial intubation
- (B) overinflation of the endotracheal tube cuff
- (C) pneumothorax
- (D) pulmonary edema
- (E) pulmonary embolism
Which of the following statements regarding latex allergy is true?
- (A) Diphenhydramine is the treatment of choice for latex-induced anaphylactic reaction
- (B) Hospital workers are at equal risk as the general population
- (C) It is more common in patients with frequent urethral catheterizations
- (D) Latex gloves can be rinsed free of antigens
- (E) Skin testing should be performed immediately after an acute reaction in the operating room
Which of the following is a complication of glycine used for irrigation during transurethral resection of the prostate?
- (A) Epileptiform activity on EEG
- (B) Peripheral neuropathy
- (C) Tachycardia
- (D) Transient blindness
- (E) Transient deafness
Which of the following is described by the standard deviation during analysis of the results of a clinical study?
- (A) Central tendency of the study results
- (B) Distribution of the results of the study group
- (C) Range of the results of the study group
- (D) Regression analysis of the study group
- (E) Statistical significance of the difference between the study groups
Two days after total abdominal hysterectomy, a 54-year-old woman develops lethargy followed by seizures and coma. Laboratory studies show a serum sodium concentration of 108 mEq/L and serum osmolality of 225 mOsm/kg. The most appropriate next step in management is administration of which of the following?
- (A) Desmopressin
- (B) Furosemide only
- (C) Saline solution 0.9% only
- (D) Furosemide and saline solution 0.9%
- (E) Furosemide and saline solution 3%
A 48-year-old woman with von Willebrand's disease is scheduled for a hysterectomy. The most appropriate initial preoperative therapy to decrease bleeding is administration of
- (A) cryoprecipitate
- (B) desmopressin (DDAVP)
- (C) fresh frozen plasma
- (D) platelets
- (E) vitamin K
Which of the following factors is the major cause of hypotension following release of the infrarenal aortic cross-clamp during aortic reconstruction?
- (A) Abnormal myocardial function
- (B) Decreased systemic vascular resistance
- (C) Down-regulation of adrenergic receptors
- (D) Increased PaCO2
- (E) Suppression of the renin-angiotensin system
A 40-year-old woman with Graves' disease is undergoing thyroidectomy with 1% isoflurane, 60% nitrous oxide, and oxygen. During surgical manipulation of the thyroid, temperature increases to 38.5°C, heart rate to 160 bpm, and blood pressure to 150/100 mmHg. The most appropriate initial treatment is to
- (A) administer dantrolene sodium
- (B) administer potassium iodide
- (C) administer propranolol
- (D) administer propylthiouracil
- (E) increase the concentration of isoflurane
Systemic hypothermia to 30°C is accompanied by
- (A) a shift to the right of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve
- (B) a decrease in carbon dioxide dissolved in plasma
- (C) a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate
- (D) an increase in MAC of volatile inhalation agents
- (E) low-voltage, high-frequency EEG pattern
Each of the following values is associated with acute tubular necrosis EXCEPT
- (A) urine osmolality of 200 mOsm/kg
- (B) urine sodium concentration of 15 mEq/L
- (C) urine specific gravity of 1.009
- (D) urine/serum osmolarity ratio of 1.2
- (E) fractional excretion of sodium of 4%
A bilateral superior laryngeal nerve block performed to facilitate fiberoptic intubation will provide anesthesia of the
- (A) base of the tongue
- (B) larynx above the vocal cords
- (C) superior surface of the epiglottis
- (D) tonsillar pillars
- (E) upper trachea
Which of the following remains normal in an otherwise healthy patient with obesity?
- (A) Alveolar PO2
- (B) Expiratory reserve volume
- (C) Functional residual capacity
- (D) Lung compliance
- (E) Static lung volumes
The trend plot shows end-tidal gases measured during a radical neck dissection. The event occurring at A is most likely
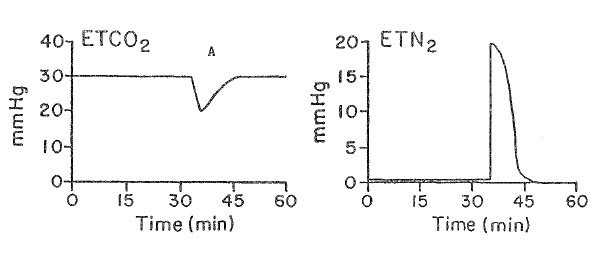
- (A) acute hypotension
- (B) endobronchial intubation
- (C) kinking of the endotracheal tube
- (D) rupture of the endotracheal cuff
- (E) venous air embolism
When used for irrigation during transurethral resection of the prostate, glycine 1.5% is associated with each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) hemolysis
- (B) hyperammonemia
- (C) cerebral edema
- (D) hypofibrinogencmia
- (E) visual disturbances
An elderly man has an acute dissection of the descending thoracic aorta. Which of the following antihypertensive therapies is most likely to extend the dissection?
- (A) Esmolol infusion
- (B) Nitroglycerin infusion
- (C) Nitroprusside infusion
- (D) Nitroprusside infusion combined with a beta-adrenergic blocker
- (E) Trimethaphan infusion
Which of the following will result in the largest change in oxygen content?
- (A) Increased hemoglobin (Hgb) concentration from 10 to 15 g/dl
- (B) Increased PaO2 from 40 to 50 mmHg (Hgb 15 g/dl)
- (C) Increased PaO2 from 60 to 70 mmHg (Hgb 15 g/dl)
- (D) Increased P50 of Hgb from 27 to 37 mmHg (Hgb 15 g/dl)
- (E) Increased pH from 7.20 to 7.40
Twenty minutes after thiopental induction for femoral herniorrhaphy, a 34-year-old woman is breathing spontaneously and receiving nitrous oxide-oxygen (2 liters each) and enflurane 3% by face mask. Pulse is 90 bpm, blood pressure is 80/60 mmHg, end-tidal enflurane concentration is 2%, and end-tidal carbon dioxide tension is 48 mmHg. Which of the following is most likely to occur on skin incision?
- (A) Pupillary dilation
- (B) Laryngeal stridor
- (C) Gross muscular movement
- (D) Increased blood pressure
- (E) No response
A morbidly obese patient is to undergo gastric stapling during general anesthesia. Following preoxygenation and induction, the oxygen saturation decreases after 40 seconds of laryngoscopy and attempted intubation. The rapid onset of arterial desaturation is most likely due to
- (A) aspiration during induction
- (B) decreased functional residual capacity
- (C) increased cardiac output
- (D) increased oxygen consumption
- (E) increased ventilatory dead space
Each of the following statements about the anatomy of the autonomic nervous system is true EXCEPT:
- (A) Preganglionic cell bodies are located in the central nervous system
- (B) Postganglionic neurons are located in outlying ganglia
- (C) The parasympathetic ganglia are located near their target organs
- (D) The adrenal gland is innervated only by the sympathetic nervous system
- (E) The parasympathetic nervous system has thoracic and sacral segments
A 58-year-old man with a history of angina is undergoing resection of an abdominal aortic aneurysm under morphine, nitrous oxide, d-tubocurarine anesthesia. Just before removal of the aortic cross-clamp, heart rate is 74 bpm, blood pressure is 115/70 mmHg, and pulmonary artery occlusion pressure is 7 mmHg. Immediately after removal of the cross-clamp, heart rate increases to 120 bpm, blood pressure decreases to 80/55 mmHg, and pulmonary artery occlusion pressure decreases to 3 mmHg. The V5 lead on the EKG demonstrates sudden ST-segment depression and T-wave inversion. Initial therapy should be
- (A) reapplication of the aortic cross-clamp
- (B) intravenous administration of sodium bicarbonate
- (C) initiation of a phenylephrine infusion
- (D) rapid expansion of blood volume by transfusion
- (E) initiation of a nitroglycerin infusion
Which of the following phenomena is primarily responsible for the decrease in core body temperature that commonly occurs during the first hour of general anesthesia?
- (A) Convective heat loss from cutaneous vasodilation
- (B) Decreased heat production
- (C) Evaporative heat loss during skin preparation
- (D) Heat loss from the respiratory tract
- (E) Redistribution of core body heat to the periphery
A 19-year-old college student is brought to the emergency department cyanotic and incoherent. Respiratory rate is 48/min, pulse is 140 bpm, and blood pressure is 140/85 mmHg. The only history obtainable is that he was at a party and suddenly felt sick. Cyanosis persists despite administration of pure oxygen by mask. A venous blood sample is chocolate-brown. The action most beneficial to the patient is to
- (A) intubate the trachea and control ventilation
- (B) perform bronchoscopy to treat foreign body aspiration
- (C) obtain a pulmonary ventilation-perfusion scan
- (D) administer methylene blue intravenously
- (E) administer thiosulfate in normal saline solution intravenously
Following pneumonectomy, a paralyzed patient being mechanically ventilated has the following arterial blood gas values: PaO2 71 mmHg, PaCO2 55 mmHg, pH 7.29. SvO2 is 45%. The most likely explanation for this SvO2 is
- (A) decreased red cell mass
- (B) high cardiac output
- (C) hypothermia
- (D) peripheral left-to-right arteriovenous shunt
- (E) ventilation / perfusion mismatch
The ECG tracing shows
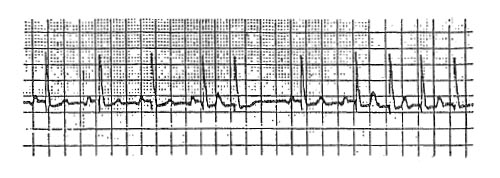
- (A) aberrant intraventricular conduction
- (B) acceleration of phase 4 depolarization of the sinus node
- (C) a compensatory pause
- (D) initiation of re-entrant supraventricular tachycardia
- (E) paroxysmal atrial fibrillation
A 69-year-old woman with mitral stenosis and atrial fibrillation is scheduled for mitral valve replacement and removal of a left atrial thrombus. After administration of pancuronium, heart rate increases to 140 bpm and blood pressure decreases to 70/40 mmHg. Which of the following is the LEAST appropriate treatment?
- (A) Cardioversion
- (B) Edrophonium
- (C) Esmolol
- (D) Phenylephrine
- (E) Verapamil
The syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion is characterized by
- (A) ADH secretion unrelated to serum osmolality
- (B) decreased ADH secretion in response to hypovolemia
- (C) highly dilute urine
- (D) hypernatremia
- (E) negative water balance
An 80-kg, 70-year-old woman is scheduled for a mastectomy. She has a history of congestive heart failure treated with digoxin 0.25 mg daily. Preoperative examination shows a sinus rhythm at 80 bpm and blood pressure of 110/70 mmHg. Laboratory studies show a serum potassium concentration of 4.2 mEq/L and a serum digoxin concentration of 1.5 mcg/ml. Five minutes after induction of general anesthesia, ventricular bigeminy is noted; blood pressure is 85/65 mmHg, SpO2 is 97%, and PetCO2, is 20 mmHg. Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
- (A) Administration of calcium chloride
- (B) Administration of ephedrine
- (C) Administration of lidocaine
- (D) Administration of potassium chloride
- (E) Decrease in ventilation
Which of the following is an effect of magnesium sulfate at the neuromuscular junction?
- (A) Augmentation of acetylcholine reuptake
- (B) Decrease in acetylcholine binding
- (C) Decrease in acetylcholine metabolism
- (D) Decrease in the prejunctional release of acetylcholine
- (E) Potentiation of the effects of ionized calcium
A 50-year-old man with alcoholism and jaundice is scheduled to undergo umbilical herniorrhaphy. An increase in which of the following best indicates impaired synthetic hepatic function?
- (A) Prothrombin time
- (B) Serum alanine aminotransferase concentration
- (C) Serum albumin/globulin ratio
- (D) Serum alkaline phosphatase concentration
- (E) Serum bilirubin concentration
During liver transplantation, venovenous bypass from the femoral and portal veins to the axillary vein during cross-clamping of the inferior vena cava
- (A) decreases urine output
- (B) prevents hypothermia
- (C) prevents metabolic acidosis
- (D) requires heparinization
- (E) supports cardiac output
During a cardiac arrest with effective chest compression and positive-pressure ventilation, 50 mEq of sodium bicarbonate is administered. Which of the following is the most likely result?
- (A) Decreased mixed venous pH
- (B) Decreased SpO2
- (C) Increased PetCO2
- (D) Increased plasma lactate concentration
- (E) Increased serum potassium concentration
Which of the following must be considered during perioperative management of a patient on long-term lithium therapy?
- (A) Intravenous fluids should include sodium
- (B) Therapy should be discontinued for 14 days prior to anesthesia
- (C) The requirement for succinylcholine is increased
- (D) The requirement for volatile anesthetics is increased
- (E) Urine output should be maintained with furosemide
A 64-year-old patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease sustained fractures of ribs 4 through 8 on the left one hour ago. Examination shows agitation, heart rate of 120 bpm, respiratory rate of 30/min, and blood pressure of 180/100 mmHg. PaO2 is 70 mmHg and PaCO2 is 35 mmHg on room air. Radiographs of the chest show no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate immediate management?
- (A) Continuous epidural analgesia using local anesthetics
- (B) Mechanical ventilation
- (C) Infusion of midazolam
- (D) Patient-controlled analgesia with morphine sulfate
- (E) Surgical stabilization of rib fractures
Following induction of general anesthesia, mask ventilation and the initial attempt at intubation is unsuccessful. Which of the following procedures is most appropriate?
- (A) Administration of additional muscle relaxant
- (B) Repeat attempt at intubation
- (C) Fiberoptic intubation
- (D) Retrograde intubation
- (E) Cricothyroidotomy
Four days after mitral valve replacement, a 49-year-old, 70-kg woman who has had oliguric renal failure since the operation requires insertion of a Schribner shunt for hemodialysis. Her BUN concentration is 104 mg/dl, serum creatinine is 9.3 mg/dl, serum sodium is 130 mEq/L, and serum potassium is 6.7 mEq/L. During the operation under local anesthesia, diazepam 7.5 mg and morphine 10 mg are administered intravenously to control agitation. Five minutes later while she is sleeping quietly, unifocal premature ventricular contractions appear at a rate of 10 per minute on the ECG monitor. The most appropriate therapy is to
- (A) administer calcium gluconate 250 mg intravenously
- (B) augment ventilation with bag and mask
- (C) administer lidocaine 100 mg intravenously
- (D) administer NaHC03 50 mEq intravenously
- (E) observe only
A patient is scheduled for right pneumonectomy. A left-sided double-lumen endobronchial tube is inserted. After the endobronchial side is clamped and both cuffs are inflated, breath sounds are heard only on the left. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Herniation of the endobronchial cuff over the carina
- (B) Occlusion of the right upper lobe bronchus
- (C) Placement of the endobronchial lumen in the left mainstem bronchus
- (D) Placement of the endobronchial lumen in the right mainstem bronchus
- (E) Placement of the endobronchial lumen in the trachea
Which of the following statements about the standard error of the mean (SE) is true?
- (A) Sample mean SE has approximately a 95% chance of containing the population mean
- (B) The SE describes the precision of the population mean
- (C) The SE describes the range of the sample values
- (D) The SE is greater than the standard deviation
- (E) The SE is obtained by multiplying the sample standard deviation by the square root of the sample size
An obese, 35-year-old man had an episode of coughing followed by vomiting during induction of anesthesia for arthroscopy of the left knee. Intense wheezing developed bilaterally over five minutes. PaO2 is 60 mmHg, PaCO2 is 42 mmHg, and pH is 7.35. Optimal management following intubation of the trachea includes
- (A) mechanical ventilation with positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), cancellation of surgery, and transfer to the intensive care unit
- (B) saline lavage and continuation of surgery using halothane anesthesia
- (C) cancellation of surgery and administration of corticosteroids and antibiotics
- (D) thorough suctioning and proceeding with halothane anesthesia
- (E) cancellation of surgery, vigorous mechanical ventilation, thorough suctioning, and administration of aminophylline
A patient with a fasting blood glucose concentration of 100 mg/dl undergoes a four-hour operation under general anesthesia without intraoperative administration of glucose. On emergence the most likely finding will be
- (A) marked hypoglycemia
- (B) mild hypoglycemia
- (C) normoglycemia
- (D) mild hyperglycemia
- (E) marked hyperglycemia
A 68-year-old man has a permanent DVI pacemaker that has been functioning appropriately. Which of the following is most likely to cause conversion to VOO pacing?
- (A) Electroconvulsive therapy
- (B) Insertion of a pulmonary artery catheter
- (C) Placement of a magnet over the pulse generator
- (D) Use of electrocautery near the pacemaker
- (E) Shivering
The most likely cause of this capnographic tracing obtained just after laryngoscopy and intubation is
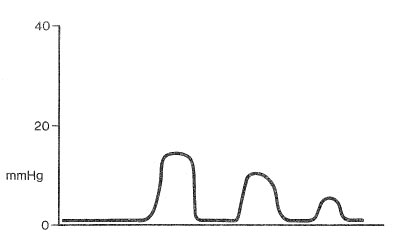
- (A) esophageal intubation
- (B) partial obstruction of the endotracheal tube
- (C) pulmonary embolus
- (D) insertion of an endotracheal nasogastric tube
- (E) mild bronchospasm
Two hours after sustaining extensive burns of the head, neck and chest in a house fire, a patient has stridor and difficulty breathing. The most appropriate management is
- (A) administration of aerosolized epinephrine
- (B) administration of helium and oxygen
- (C) endotracheal intubation
- (D) intravenous injection of dexamethasone
- (E) tracheostomy
Each of the following is an effect of electroconvulsive therapy EXCEPT
- (A) increased intracranial blood volume
- (B) increased oxygen consumption
- (C) inhibition of parasympathetic activity
- (D) retrograde amnesia
- (E) stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system
A 32-year-old man is scheduled for hernia repair. He underwent heart transplantation for cardiomyopathy five years ago. Which of the following findings is most likely?
- (A) Absence of coronary atherosclerosis
- (B) Biventricular hypokinesis on echocardiography
- (C) Down-regulation of cardiac beta-adrenergic receptors
- (D) Increased heart rate at rest
- (E) Right ventricular hypertrophy
Which of the following situations is most likely related to paraplegia following repair of a descending thoracic aortic aneurysm?
- (A) Decreased cerebrospinal fluid pressure
- (B) Epidural hematoma
- (C) Hypertension proximal to the aortic cross clamp
- (D) Improper placement of surgical retractors
- (E) Prolonged aortic cross-clamp time
A 76-year-old man has a leaking abdominal aortic aneurysm. His blood pressure and pulse have remained stable for 15 minutes at 90/60 mmHg and 130 bpm, respectively. His hemoglobin concentration is 11 g/dl, and the EKG shows a left bundle branch block. Induction of anesthesia should proceed
- (A) after a pulmonary artery catheter has been inserted and the pulmonary artery occlusion pressure is greater than 7 mmHg
- (B) when the pulse has decreased below 130 bpm from the rapid transfusion of blood
- (C) when systolic blood pressure has increased to more than 120 mmHg from the rapid infusion of lactated Ringer's solution
- (D) immediately on arrival in the operating room
- (E) when circulatory signs deteriorate or cease to improve with rapid volume expansion
A patient undergoes thoracotomy in the lateral decubitus position. Which of the following maneuvers is most likely to increase PaO2 during one-lung ventilation?
- (A) Applying continuous positive airway pressure to the nondependent lung
- (B) Applying positive end-expiratory pressure to the dependent lung
- (C) Increasing inspiratory flow rate
- (D) Increasing the tidal volume
- (E) Increasing the ventilatory rate
A previously healthy 46-year-old woman has severe substernal chest pain one hour after receiving morphine sulfate 10 mg intramuscularly for an elective cholecystectomy. Vital signs, SpO2, and findings on a five-lead ECG on the operating room monitor are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- (A) Sublingual administration of nitroglycerin
- (B) Intravenous administration of butorphanol
- (C) Intravenous administration of naloxone
- (D) Cardiology consultation
- (E) Cancellation of surgery
Two months ago a 68-year-old man with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus had a transurethral resection of the prostate under spinal anesthesia with tetracaine plus epinephrine. He now has numbness and tingling in both feet and disturbance of gait. Physical examination demonstrates stocking-type hypesthesia of both feet and ankles. The most likely diagnosis is
- (A) anterior spinal artery syndrome
- (B) diabetic neuropathy
- (C) adhesive arachnoiditis
- (D) cauda equina syndrome
- (E) peripheral nerve injury from the lithotomy position
A 57-year-old man with hepatocellular disease is scheduled to undergo a colectomy for colon cancer. Preoperative laboratory studies show a plasma albumin concentration of 2.4 g/dl (normal = 3.5 to 5.5 g/dl); prothrombin time is 16 sec (control 12 sec). Which of the following statements concerning the anesthetic management of this patient is true?
- (A) Atracurium will have a prolonged duration of action
- (B) The risk for perioperative hyperglycemia is increased
- (C) Mivacurium will have a shortened duration of action
- (D) The unbound fraction of thiopental will be increased
- (E) Vitamin K injection will normalize the prothrombin time
Hypothermia to 29°C will decrease
- (A) hematocrit
- (B) plasma fibrinogen concentration
- (C) plasma pH
- (D) plasma protein concentration
- (E) platelet function
Which of the following is the most likely cause of a decrease in end-tidal carbon dioxide tension during general anesthesia with a constant minute ventilation?
- (A) Administration of sodium bicarbonate
- (B) Intravenous administration of hypertonic glucose solution
- (C) Decrease in cardiac output
- (D) Decrease in fresh gas flow in a Bain circuit
- (E) Malfunction of the inspiratory valve in a circle system
The use of glycine as irrigating solution during transurethral resection of the prostate could be associated with each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) ammonia toxicity
- (B) coma
- (C) hemolysis
- (D) hyponatremia
- (E) transient blindness
A healthy 60-kg 52-year-old woman undergoing reduction mammoplasty is anesthetized with isoflurane and oxygen, and deliberate hypotension to 80/40 mmHg is induced with nitroprusside. Urine output through an indwelling urethral catheter has been 10 mL during the past hour. You should now
- (A) administer furosemide 40 mg intravenously
- (B) infuse normal saline solution until urine output reaches 35 mL/hr
- (C) administer dopamine at 3 mcg/kg/min
- (D) expect normal urine flow with restoration of normal blood pressure
- (E) discontinue nitroprusside administration
A 67-year-old man is undergoing total hip replacement under general anesthesia. He had a permanent endocardial VVI pacemaker placed two years ago for complete heart block, and since arrival in the operating room has been paced continuously. Use of the electrocautery causes the pacemaker to malfunction intermittently. The most appropriate management is to
- (A) tape a magnet over the pacemaker generator and convert to asynchronous mode
- (B) do nothing since the pacemaker is programmed to deal with this circumstance
- (C) stop the surgeon from using the electrocautery
- (D) limit the surgeon to 10 sec/min electrocautery bursts
- (E) place the electrocautery indifferent lead as close as possible to the pacemaker
Each of the following decreases hepatic blood flow EXCEPT
- (A) isoflurane anesthesia
- (B) spinal anesthesia
- (C) hypercarbia
- (D) mechanical ventilation
- (E) positive end-expiratory pressure
Each of the following changes is expected with deliberate hypothermia EXCEPT
- (A) decreased unloading of oxygen from hemoglobin
- (B) a 5% decrease in MAC for each 1°C decrease in temperature
- (C) increased arterial oxygen and carbon dioxide contents
- (D) a 50% decrease in cerebral metabolic rate at 28°C
- (E) spike and dome EEG activity at temperatures below 30°C
A 19-year-old man is undergoing inguinal herniorrhaphy. He is anesthetized with a spinal block supplemented with midazolam and fentanyl. During the procedure, he has sudden loss of consciousness, profound hypotension, and bradycardia; systolic pressure is 40 mmHg and heart rate is 30 bpm. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is started. The most appropriate next step is administration of
- (A) atropine
- (B) ephedrine
- (C) epinephrine
- (D) flumazenil
- (E) naloxone
Pulsus paradoxus is commonly seen during anesthesia in patients with each of the following conditions EXCEPT
- (A) severe asthma
- (B) right-sided heart failure
- (C) hypovolemia
- (D) atrial septal defect
- (E) obesity
In a patient with hypovolemic shock, which of the following factors is the best measure of the overall balance between oxygen supply and demand?
- (A) Arterial oxygen content
- (B) PetO2
- (C) Mixed venous oxygen saturation
- (D) PaO2
- (E) Transcutaneous oxygen tension
A 40-year-old man is undergoing open reduction and internal fixation of a fractured femur. During anesthesia with fentanyl, sevoflurane, and oxygen, heart rate decreases to 20 bpm and 6 premature ventricular contractions per minute are noted. No pulse is detected. The most appropriate next step is to
- (A) administer atropine
- (B) administer epinephrine
- (C) administer lidocaine
- (D) apply a transthoracic pacemaker
- (E) start cardiopulmonary resuscitation
A 56-year-old woman with pulmonary fibrosis is scheduled for pneumonectomy. Which of the following parameters best predicts potential postoperative functional impairment?
- (A) Exercise tolerance
- (B) Flow-volume loop
- (C) Resting arterial blood gas values
- (D) Unilateral pulmonary artery occlusion pressure
- (E) Vital capacity and FEV,
An adult patient with atrial fibrillation develops pulseless ventricular tachycardia wfiile undergoing synchronized electirical cardioversion. Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
- (A) Intravenous administration of adenosine
- (B) Intravenous administration of a bolus of lidocaine followed by electrical cardioversion
- (C) Immediate repeat synchronized cardioversion at the same energy level
- (D) Immediate repeat synchronized cardioversion at twice the previous energy level
- (E) Unsynchronized electrical cardioversion
During laser microsurgery of the larynx using an endotracheal tube, a fire occurs in the airway. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management?
- (A) Increase FiO2 to 1.0
- (B) Instill saline into the endotracheal tube
- (C) Perform cricothyroidotomy
- (D) Remove the endotracheal tube
- (E) Ventilate with air
A 120-kg 56-year-old man undergoing gastrectomy during anesthesia with fentanyl and isoflurane has a PetCO2 of 35 mmHg and a PaCO2 of 50 mmHg. His FEV,/FVC ratio is 80% of predicted. Heart rate is 120 bpm and arterial blood pressure is 80/40 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the difference in PaCO2 and PetCO2?
- (A) Aspiration pneumonitis
- (B) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- (C) Decreased cardiac output
- (D) Decreased VD/VT ratio
- (E) Increased QS/QT ratio
A patient with cirrhosis presenting for liver transplantation is likely to exhibit each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) decreased cardiac output
- (B) decreased serum glucose concentration (0 decreased serum sodium concentration
- (D) decreased systemic vascular resistance
- (E) increased alveolar-arterial oxygen tension difference
A healthy 57-year-old man with a ureteral calculus is scheduled for immersion extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. Which of the following statements is true?
- (A) Delivery of the shock wave is timed by the R wave of the ECG
- (B) Continuous epidural anesthesia is contraindicated because of the risk for infection
- (C) If a regional technique is used, a T10 sensory level is required for adequate anesthesia
- (D) If general anesthesia is used, high tidal volumes and low respiratory rate are preferred
- (E) Removal of the patient from the bath is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure
A 23-year-old man who is receiving his first anesthetic has not resumed spontaneous ventilation two hours after receiving succinylcholine. The train-of-four monitor shows no twitch response. Which of the following is the most likely cholinesterase genotype in this patient?
- (A) Atypical : atypical
- (B) Fluoride-resistant : fluoride-resistant
- (C) Fluoride-resistant : silent
- (D) Normal : normal
- (E) Normal : silent
Each of the following conditions is a complication of mediastinoscopy EXCEPT
- (A) air embolism
- (B) hemorrhage
- (C) injury to the left recurrent laryngeal nerve
- (D) occlusion of the left carotid artery
- (E) tension pneumothorax
The patient at LEAST risk of pulmonary aspiration of gastric contents during induction of anesthesia is
- (A) markedly obese and NPO for eight hours
- (B) fed black coffee four hours before elective surgery
- (C) scheduled for elective cesarean delivery and NPO for 20 hours
- (D) NPO for four hours after a full meal
- (E) scheduled for elective repair of a hiatus hernia
A 72-year-old woman is somnolent one day after left carotid endarterectomy. She has smoked 2 packs of cigarettes daily for 50 years. Six weeks ago, she underwent right carotid endarterectomy. At this time, arterial blood gases while breathing room air are PO2, 45 mmHg, PCO2, 60 mmHg, and pH 7.30. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the increased PCO2?
- (A) Bilateral vocal cord paralysis
- (B) Cerebral infarction
- (C) Congestive heart failure
- (D) Denervation of the carotid bodies
- (E) Phrenic nerve injury
Following transfusion of packed red blood cells during general anesthesia, the patient's blood pressure decreases, heart rate and temperature increase, and hemoglobinuria and diffuse oozing are observed. Which of the following is the most appropriate first step in management?
- (A) Administration of hydrocortisone
- (B) Administration of fresh frozen plasma
- (C) Administration of epsilon-aminocaproic acid
- (D) Rapid infusion of crystalloid
- (E) Transfusion of platelet concentrates
A 50-year-old woman develops stridor 10 hours after undergoing thyroidectomy. The most appropriate management is administration of which of the following drugs?
- (A) Albuterol
- (B) Calcium chloride
- (C) Ipratropium bromide
- (D) Racemic epinephrine
- (E) Triiodothyronine
Bronchospasm occurring during anesthesia in a patient with an ileal carcinoid is best treated by administration of
- (A) aminophylline
- (B) dexamethasone
- (C) halothane
- (D) ketamine
- (E) somatostatin
A 77-year-old woman is still intubated and breathing spontaneously following a total hip replacement. The muscle relaxant has been reversed. Tidal volume is 400 ml, end-tidal carbon dioxide tension is 45 mmHg, and SpO2 is 98% at an FiO2 of 1.0. On transfer from the operating table to the gurney, heart rate increases from 65 to 100 bpm and blood pressure decreases from 130/80 to 80/50 mmHg. End-tidal carbon dioxide tension is 30 mmHg and SpO2 is 94%. The most likely diagnosis is
- (A) anaphylactic reaction
- (B) bronchospasm
- (C) myocardial infarction
- (D) pulmonary embolism
- (E) unreplaced blood loss
In the absence of coronary artery disease, isoflurane-induced vasodilation and tachycardia are beneficial hemodynamic goals for which of the following cardiac diseases?
- (A) Aortic regurgitation
- (B) Aortic stenosis
- (C) Asymmetric septal hypertrophy (IHSS)
- (D) Mitral stenosis
- (E) Pulmonary regurgitation
A 90-kg, 59-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is undergoing laparotomy. Mechanical ventilation is being carried out with a fresh gas flow of 2 L/min at a rate of 16/min and tidal volume of 900 ml; I:E ratio is 1:2.5. PaCO2 remains greater than 50 mmHg. Preoperative PaCO2, was normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- (A) Adding 10 cmH20 of positive end-expiratory pressure
- (B) Converting to spontaneous ventilation
- (C) Decreasing inspiratory flow rate
- (D) Increasing exhalation time
- (E) Increasing fresh gas flow
Which of the following statements concerning carbon monoxide poisoning is true?
- (A) Diagnosis is excluded if the PaO2 is greater than 300 mmHg while breathing 100% oxygen
- (B) Increased inspired oxygen concentration accelerates displacement of carbon monoxide from hemoglobin
- (C) Methylene blue decreases binding of carbon monoxide to hemoglobin
- (D) Pulse oximetry accurately reflects hemoglobin oxygen saturation
- (E) Tissue oxygen delivery is normal
A man with alcoholic cirrhosis and a hemoglobin concentration of 10 g/dl has an intraoperative PaO2 of 75 mmHg at an FiO2 of 0.5. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the low PaO2?
- (A) Anemia
- (B) Decreased cardiac output
- (C) Increased dead space
- (D) Intrahepatic arteriovenous shunts
- (E) Intrapulmonary arteriovenous shunts
A 64-year-old man with diabetes mellitus well controlled with NPH insulin undergoes lower extremity revascularization. Following administration of protamine 10 mg, the patient has facial flushing and blood pressure of 60/30 mmHg. The most appropriate initial step in management is administration of which of the following drugs?
- (A) Diphenhydramine
- (B) Epinephrine
- (C) Hydrocortisone
- (D) Norepinephrine
- (E) Phenylephrine
A patient who is scheduled for emergency laparotomy for bowel obstruction has had oliguria for three hours. She has had hypertension for 10 years. Which of the following laboratory findings would indicate preoperative fluid challenge?
- (A) Urine osmolality: 300 mOsm/L
- (B) Urine specific gravity: 1.015
- (C) Urine sodium concentration: 35 mmol/L
- (D) Fractional excretion of sodium: 0.5
- (E) Ratio of urine-to-plasma creatinine concentrations: 8
When evaluating a screening test, which of the following is the most appropriate term for the proportion of patients with a disease who have a positive test result?
- (A) Accuracy
- (B) Incidence
- (C) Selectivity
- (D) Sensitivity
- (E) Specificity
Pulsus paradoxus is commonly seen during anesthesia in patients with each of the following conditions EXCEPT
- (A) severe asthma
- (B) right-sided heart failure
- (C) hypovolemia
- (D) atrial septal defect
- (E) obesity
Each of the following values is associated with acute tubular necrosis EXCEPT
- (A) urine osmolality of 200 mOsm/L
- (B) urine sodium concentration of 15 mEq/L
- (C) urine specific gravity of 1.009
- (D) urine/serum osmolality ratio of 1.2
- (E) fractional excretion of sodium of 4%
A 39-year-old patient with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus receives thiopental 250 mg and succinylcholine 80 mg and is ventilated with 0.75% isoflurane in oxygen. Arterial pressure decreases abruptly from 140/100 to 80/50 mmHg while heart rate remains unchanged at 70 bpm. Failure of heart rate to increase most likely results from
- (A) acute hypoglycemia
- (B) autonomic neuropathy
- (C) depression of sinus node function by thiopental
- (D) depression of the baroreflex response by isoflurane
- (E) ganglionic stimulation by succinylcholine
Which of the following is the most common initial sign of hemolytic transfusion reaction during general anesthesia?
- (A) Bronchospasm
- (B) Diffuse bleeding
- (C) Fever
- (D) Hemoglobinuria
- (E) Hypotension
A 30-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being rescued from a house fire. With the trachea intubated and FiO2 at 1.0, arterial blood gas values are PaO2 495 mmHg, PaCO2 28 mmHg, and pH 7.28. Hemoglobin saturation measured by co-oximeter is 50%. The most appropriate next step is to
- (A) add positive end-expiratory pressure
- (B) add n-acetylcysteine to the inhaled gases
- (C) administer sodium bicarbonate intravenously
- (D) transfuse 2 units of packed red blood cells
- (E) transfer to a hyperbaric chamber
Which of the following is increased in patients with chronic anemia?
- (A) Mixed venous oxygen content
- (B) P50
- (C) Pulmonary vascular resistance
- (D) Systemic vascular resistance
- (E) Blood viscosity
A 30-year-old woman undergoes thyroidectomy under general endotracheal anesthesia. Immediately after extubation while breathing spontaneously, she has laryngospasm that resolves after 60 seconds of continuous positive airway pressure applied by face mask. In the PACU, she develops shortness of breath, tachypnea, hypoxemia, and rales. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- (A) Gastric acid aspiration
- (B) Myocardial infarction
- (C) Pulmonary edema
- (D) Pulmonary embolism
- (E) Vocal cord paralysis
A 65-year-old patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy has chest pain prior to induction of anesthesia. Pulse is 80 bpm and blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg. The ECG (V5) shows sinus rhythm and new ST-segment depression. The most appropriate management is administration of
- (A) furosemide
- (B) metoprolol
- (C) morphine
- (D) nifedipine
- (E) nitroglycerin
During transurethral resection of the prostate under spinal anesthesia with a sensory level to T10, a patient has sudden onset of sharp upper abdominal pain and nausea. Arterial blood pressure increases from 120/80 to 150/90 mmHg; the patient becomes diaphoretic. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- (A) Bladder perforation
- (B) Hemolysis
- (C) Hypervolemia
- (D) Hyponatremia
- (E) Myocardial ischemia
Which of the following abnormalities in serum is most likely to result from intraoperative discontinuation of parenteral hyperalimentation?
- (A) Hypocalcemia
- (B) Hypocarbia
- (C) Hypoglycemia
- (D) Hypokalemia
- (E) Hyponatremia
During induction of anesthesia, a 56-year-old man with small bowel obstruction vomits a large quantity of undigested food particles and presumably aspirates. After instituting ventilation with pure oxygen, the most appropriate management is to
- (A) administer dexamethasone
- (B) administer penicillin G
- (C) perform bronchoscopy
- (D) ventilate with positive end-expiratory pressure 15 cmH2O
- (E) proceed with the anesthesia plan if the tracheal pH is greater than 2.5
Which of the following postoperative treatments decreases the risk for deep venous thrombosis?
- (A) Blood transfusion
- (B) Epidural anesthesia
- (C) Etomidate
- (D) Ketorolac
- (E) Patient-controlled analgesia
Assignment of a patient to an ASA physical status category is used to
- (A) facilitate comparisons among different patient groups and institutions
- (B) guide the choice of anesthetic technique
- (C) permit accurate determination of charges for professional services
- (D) predict anesthetic risk
- (E) predict perioperative mortality
You are called to a witnessed cardiac arrest where cardiopulmonary resuscitation is being performed. After successful intubation, arterial blood gas values are PaO2 86 mmHg, PaCO2 63 mmHg, and pH 7.25 at an FiO2 of 1.0. The most appropriate management at this time is to
- (A) repeat arterial blood gas analysis using a new specimen
- (B) administer sodium bicarbonate
- (C) administer fluid challenge with 500 ml of normal saline solution
- (D) hyperventilate the patient
- (E) add positive end-expiratory pressure
Which of the following statements concerning carbon monoxide poisoning is true? A 38-year-old woman with a large goiter has undergone subtotal thyroidectomy. Airway obstruction is noted immediately after extubation despite normal vocal cord function on laryngoscopy. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
- (A) Arytenoid dislocation
- (B) Hematoma
- (C) Hypocalcemia
- (D) Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury
- (E) Tracheomalacia
Which of the following statements best describes the decrease in functional residual capacity that accompanies the induction of general anesthesia?
- (A) It does not change compliance
- (B) It is greater with spontaneous ventilation than with controlled ventilation
- (C) It is independent of body position
- (D) It is not corrected by application of positive end-expiratory pressure
- (E) It occurs within the first 10 minutes of anesthesia
A 26-year-old patient with multiple trauma is admitted to the intensive care unit postoperatively. The early development of polyuria, hypotension, low urine sodium excretion, high serum osmolality, and normal serum creatinine concentration is best explained by
- (A) adrenal insufficiency
- (B) fluoride-induced high-output renal failure
- (C) inappropriate ADH secretion
- (D) intraoperative fluid overload
- (E) posterior pituitary insufficiency
The most common early indication of drug dependence in an anesthesiologist is
- (A) a positive finding on random screening of urine
- (B) inconsistency between anesthetic and drug control records
- (C) change in behavior
- (D) incapacitation due to overdose
- (E) the presence of needle tracks on the extremities
An unconscious adult patient is being ventilated through an esophageal obturator airway (EOA) in the emergency department. In the absence of cervical spine injury, which of the following is appropriate?
- (A) Use of the EOA for airway management until the patient regains consciousness
- (B) Removal of the EOA before insertion of an endotracheal tube
- (C) Placement of an endotracheal tube before removal of the EOA
- (D) Removal of the EOA under fiberoptic endoscopic visualization
- (E) Cricothyroidotomy
A 68-year-old man has signs of a coagulopathy after receiving 10 units of packed erythrocytes during emergency repair of a leaking abdominal aortic aneurysm. The most likely cause is
- (A) depletion of factor V
- (B) disseminated intravascular coagulation
- (C) hypothermia
- (D) platelet dysfunction
- (E) thrombocytopenia
Which of the following is most likely to increase hepatic blood flow during general anesthesia?
- (A) Addition of positive end-expiratory pressure
- (B) Discontinuation of isoflurane and administration of enflurane
- (C) Increased PaCO2
- (D) Moderate controlled hypotension
- (E) Subarachnoid administration of morphine
Which of the following statements concerning myasthenia gravis is true?
- (A) Neostigmine is inappropriate for antagonism of neuromuscular blockade
- (B) The number of acetylcholine receptors is decreased
- (C) Plasma cholinesterase concentration is decreased
- (D) The risk for malignant hyperthermia is increased
- (E) Succinylcholine is contraindicated
Which of the following is the most appropriate initial therapy for acute pulmonary hypertension with right ventricular dysfunction and severe systemic hypotension that occurs during anesthesia?
- (A) Amrinone
- (B) Epinephrine
- (C) Isoflurane
- (D) Isoproterenol
- (E) Nitroglycerin
A 70-year-old man who underwent bilateral carotid endarterectomies two years ago is to undergo anesthesia and surgery. The denervation of the carotid bodies is likely to result in
- (A) chronic respiratory alkalosis
- (B) decreased ventilatory response to hypoxemia
- (C) increased ventilatory response to hypercarbia
- (D) labile hypertension
- (E) resting bradycardia
A patient being mechanically ventilated in the ICU requires wound debridement twice daily. Each of the following agents would be appropriate for induction of brief general anesthesia EXCEPT
- (A) nitrous oxide
- (B) etomidate
- (C) ketamine
- (D) methohexital
- (E) midazolam
In clinical anesthesia practice, the term "informed consent" is best described as a legal concept in which patients
- (A) agree to anesthesia care based on full disclosure of facts needed to make the decision intelligently
- (B) are told of all possible risks of anesthesia and anesthetic procedures
- (C) delegate all decisions regarding anesthesia care to the anesthesiologist
- (D) release the physicians from liability
- (E) sign global consent forms for surgical procedures that cover the administration of anesthesia care
A patient who had liver transplantation two years ago now requires general anesthesia for ENT surgery. Minimal rejection has occurred on a regimen of cyclosporine and prednisone. Which of the following is most likely?
- (A) Hypoalbuminemia
- (B) Hypocalcemia
- (C) Episodic hypoglycemia
- (D) Increased serum creatinine concentration
- (E) Prolonged prothrombin time
A 72-year-old man has massive venous hemorrhage during a radical prostatectomy. Blood pressure decreases from 110/60 to 75/30 mmHg and central venous pressure decreases from 12 to 4 mmHg. End-expiratory carbon dioxide tension decreases from 34 to 24 mmHg during constant minute ventilation. The most appropriate next step should be to
- (A) apply positive end-expiratory pressure to the breathing circuit
- (B) attempt to aspirate air from the central venous catheter
- (C) expand intravascular volume
- (D) place the patient in the Trendelenburg position
- (E) turn the patient to the left lateral decubitus position
A 28-year-old woman undergoes total thyroidectomy. The left recurrent laryngeal nerve is transected during the procedure. Which of the following findings is most likely postoperatively?
- (A) Normal voice
- (B) Aphonia
- (C) Hoarseness
- (D) Expiratory stridor
- (E) Inspiratory stridor
A 30-year-old man who is undergoing laparotomy and resection of a large kidney tumor has a decrease in SpO2 from 100% to 92% and an increase in peak airway pressure from 20 to 35 cm H2O. Plateau pressure is unchanged at 18 cm H2O. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Abdominal packing
- (B) Inadequate anesthesia
- (C) Inadequate muscle relaxation
- (D) Obstruction of the endotracheal tube
- (E) Pneumothorax
Which of the following is the most likely cause of the increased incidence of right ventricular failure in patients with morbid obesity?
- (A) Chronic hypoxia
- (B) Chronic silent pulmonary aspiration
- (C) Chronic silent subendocardial ischemia
- (D) Decreased vital capacity
- (E) Increased pulmonary blood flow
A 25-year-old woman undergoes a difficult open cholecystectomy during anesthesia with isoflurane, nitrous oxide, fentanyl, and vecuronium. Five units of blood are administered intraoperatively. Two days later, the patient has mildly increased serum transaminase concentrations and markedly increased alkaline phosphatase and direct bilirubin concentrations. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Acute viral hepatitis
- (B) Hemolysis
- (C) Isoflurane-induced liver dysfunction
- (D) Retained common duct stone
- (E) Sepsis
Nitroprusside therapy for hypertension should be discontinued in the presence of
- (A) acute myocardial infarction
- (B) increasing metabolic acidosis
- (C) methemoglobinemia
- (D) mitral regurgitation
- (E) renal failure
During induction of general anesthesia in a patient with a supraglottic tumor, both intubation and subsequent ventilation via a face mask are impossible. A cricothyroidotomy is performed with a 16-gauge intravenous catheter. Which of the following statements is true?
- (A) Application of pressures greater than 35 cmH2O to the catheter will increase the risk for pulmonary barotrauma
- (B) PaC02 can be maintained at a normal level using a standard circle system attached to the catheter
- (C) PaO2 greater than 100 mmHg can be maintained indefinitely using transtracheal jet ventilation with pure oxygen through the catheter
- (D) Emergency surgical tracheostomy would have improved the likelihood of survival
- (E) The presence of this tumor contraindicates jet ventilation via cricothyroidotomy
Each of the following conditions is associated with autonomic hyperreflexia in patients with spinal cord injury EXCEPT
- (A) bradycardia
- (B) flushing below the level of injury
- (C) headache
- (D) sweating above the level of injury
- (E) systolic hypertension
Addition of 20 cmH2O positive end-expiratory pressure to a patient receiving controlled mechanical ventilation decreases cardiac output and left ventricular function by
- (A) increasing right ventricular preload
- (B) increasing right ventricular afterload
- (C) increasing left ventricular preload
- (D) increasing left ventricular afterload
- (E) producing myocardial ischemia
A 27-year-old man with a one-month history of quadriplegia at a C6 level is given general anesthesia for cystoscopy. During the cystoscopy, blood pressure suddenly increases to 220/120 mmHg. Further evaluation is most likely to show
- (A) atrial fibrillation (ventricular rate 100 bpm)
- (B) paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (150 bpm)
- (C) sinus bradycardia
- (D) piloerection above the level of C6
- (E) sweating above the level of C6
The ECG strip shown is recorded as a patient with a permanent transvenous DDD pacemaker enters the operating room. These changes indicate that the pacemaker is
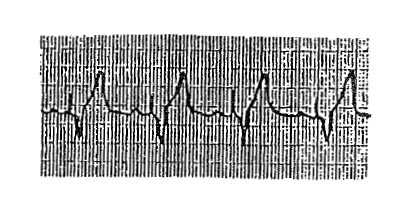
- (A) sensing the T waves
- (B) sensing the retrograde P waves
- (C) triggering off the intrinsic atrial activity
- (D) malfunctioning in the atrial pacing mechanism
- (E) prematurely stimulating the ventricle
A 33-year-old woman is scheduled for emergency appendectomy under general anesthesia. She has hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and has had two episodes of syncope in the past year. Which of the following statements concerning anesthetic management is true?
- (A) Spinal anesthesia is preferred to general anesthesia
- (B) Deep levels of isoflurane anesthesia are appropriate
- (C) Fluid administration should be restricted
- (D) Phenylephrine is preferred to ephedrine to treat hypotension
- (E) Positive end-expiratory pressure will decrease left ventricular outflow obstruction
Six hours after coronary artery bypass grafting, a pulmonary artery catheter oximeter shows a mixed venous hemoglobin oxygen saturation of 50%. This value may result from each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) anemia
- (B) fever
- (C) hypovolemia
- (D) respiratory alkalosis
- (E) shivering
A middle-aged, 70-kg man with a brain tumor is scheduled for an elective craniotomy. Preoperatively, he is alert but papilledema is present. Anesthesia is induced with thiopental 300 mg and succinylcholine 100 mg, followed by tracheal intubation. Immediately following intubation vigorous bucking occurs. The best immediate management would be to
- (A) administer succinylcholine 100 mg intravenously
- (B) administer fentanyl 500 jug intravenously
- (C) hyperventilate with isoflurane 2%
- (D) administer thiopental 400 mg intravenously
- (E) hyperventilate and administer lidocaine 1 mg/kg intravenously
Which of the following findings would be considered normal in the EEG of an adult?
- (A) Decreased frequency during induction with halogenated anesthetics
- (B) Decreased frequency in frontal areas with administration of nitrous oxide 50%
- (C) Dominance of beta rhythm at 20 to 30 Hz during the awake relaxed state
- (D) Electrical silence with administration of isoflurane 2.5 MAC
- (E) The presence of burst-suppression during natural sleep
Following extubation after nasotracheal intubation for seven days, a 35-year-old man has fever, facial pain, nasal stuffiness, and purulent nasal secretions. The most likely cause is
- (A) eustachian tube obstruction
- (B) frontal sinusitis
- (C) maxillary sinusitis
- (D) parotiditis
- (E) retropharyngeal abscess
During controlled ventilation, which of the following will cause an increase in end-tidal carbon dioxide tension with a normal waveform on the capnograph?
- (A) Bronchospasm
- (B) Rapid blood loss
- (C) Ventricular fibrillation
- (D) Endobronchial migration of the endotracheal tube
- (E) Release of a thigh tourniquet
Which of the following findings on the left is most likely to be associated with an increased risk of complications with cannulation of the left internal jugular vein compared with cannulation of the right internal jugular vein?
- (A) Longer recurrent laryngeal nerve
- (B) Lower location of the cupola of the pleura
- (C) More acute angle between the internal jugular and innominate veins
- (D) More anterior location of the phrenic nerve
- (E) Presence of the thoracic duct
A patient is undergoing exploration of a stab wound to the left side of the neck. On awake laryngoscopy, the left vocal cord is in midposition and the right vocal cord is abducted during inspiration. The most likely cause of these findings is trauma to which of the following structures on the left?
- (A) C7-8 nerve root
- (B) Stellate ganglion
- (C) Glossopharyngeal nerve
- (D) Superior laryngeal nerve
- (E) Vagus nerve
During anesthesia with nitrous oxide and isoflurane in a 70-kg, 25-year-old patient, airway resistance would be decreased by
- (A) a decrease in lung volume
- (B) insertion of a 9-mm endotracheal tube
- (C) administration of atropine
- (D) neuromuscular block with d-tubocurarine
- (E) movement of the patient from the supine to the sitting position
The tracing indicates that the pacemaker generator is
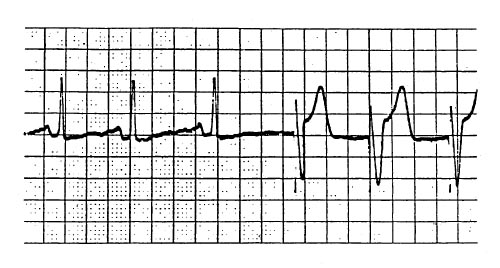
- (A) malfunctioning
- (B) VVT sensing and capturing normally
- (C) VOO sensing and capturing normally
- (D) DVI sensing and capturing normally
- (E) VVI sensing and capturing normally
During one-lung ventilation, each of the following affects hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in the nonventilated lung EXCEPT
- (A) application of continuous positive airway pressure to the nonventilated lung
- (B) high alveolar pO2 in the ventilated lung
- (C) infusion of isoproterenol
- (D) low mixed venous pO2
- (E) pulmonary hypertension
Compared with healthy nonhypertensive patients, in patients with untreated hypertension undergoing anesthesia and operation,
- (A) cerebral ischemia may occur at higher blood pressures
- (B) intravenous fluid should be restricted before induction
- (C) left ventricular hypertrophy enhances compensation for intraoperative fluid loss
- (D) responses to sympathetic stimulation are decreased
- (E) the incidence of intraoperative hypotension is lower
A 45-year-old man is scheduled for appendectomy under general anesthesia. He reports that for many years he has occasionally felt his heart "skip a beat." The ECG tracing shown was obtained one hour ago. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
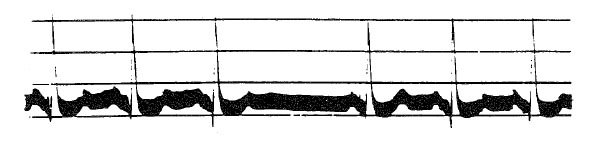
- (A) Proceeding with induction of anesthesia
- (B) Administration of a loading dose of digoxin
- (C) Carotid sinus massage
- (D) Intravenous administration of atropine
- (E) Placement of a temporary pacemaker
Each of the following is a recognized complication during a transurethral resection for which glycine is used as an irrigant EXCEPT
- (A) disseminated intravascular coagulopathy
- (B) hemolysis
- (C) hyperammonemia
- (D) shoulder pain
- (E) transient blindness
A 30-year-old man receives spinal anesthesia to the level of T4. Ten minutes later, heart rate and blood pressure abruptly decrease to 30 bpm and 60/25 mmHg, respectively. The most appropriate management is administration of which of the following drugs?
- (A) Atropine
- (B) Epinephrine
- (C) Isoproterenol
- (D) Metaraminol
- (E) Phenylephrine
A 46-year-old man is scheduled for repair of an inguinal hernia. Six years ago, he had an episode of malignant hyperthermia during cholecystectomy. Which of the following is the most appropriate perioperative management?
- (A) Administration of a regional anesthetic
- (B) Administration of dantrolene orally for two days prior to surgery
- (C) Avoidance of all inhalational anesthetics except isoflurane
- (D) Avoidance of ester local anesthetics
- (E) Flushing the anesthesia machine with oxygen 10 L/min for a minimum of 12 hours
A 35-year-old woman with systemic lupus erythematosus is admitted to the critical care unit following sudden onset of severe chest pain. Examination shows tachycardia, hypotension, pulmonary edema, and a blowing systolic murmur in the left parasternal region. The most appropriate management is
- (A) aerosol administration of terbutaline
- (B) intravenous infusion of phenylephrine and nitroglycerin
- (C) intravenous infusion of esmolol
- (D) intravenous infusion of epinephrine and nitroprusside
- (E) volume loading with lactated Ringer's solution
After the first 70 minutes of a transurethral resection of the prostate, a 70-year-old man becomes confused and has tachycardia, hypertension, and shortness of breath. Serum sodium concentration is 116 mEq/L. After informing the surgeon that the procedure should be terminated as soon as possible, the most appropriate next step would be to
- (A) administer furosemide
- (B) administer labetalol
- (C) administer 3% sodium chloride
- (D) change the irrigating solution to normal saline
- (E) induce general endotracheal anesthesia
A 70-year-old man undergoes cross clamping of the aorta for repair of an abdominal aneurysm. Which of the following methods is most appropriate for decreasing hypotension associated with removal of the cross clamp?
- (A) Administration of a phenylephrine bolus when the cross clamp is removed
- (B) Correction of any base deficit with sodium bicarbonate during clamping
- (C) Decrease of anesthetic to allow blood pressure to increase to 20% above preclamp levels
- (D) Volume loading to increase pulmonary artery occlusion pressure prior to removal
- (E) Infusion of dopamine 10 minutes prior to removal
During a right lower lobe resection, SpO2 decreases from 99% to 70% after institution of one-lung ventilation. FiO2 is 1.0. The most appropriate management is to
- (A) administer an inhaled bronchodilator
- (B) apply continuous positive airway pressure to the right lung
- (C) apply positive end-expiratory pressure to the left lung
- (D) increase tidal volume
- (E) reinflate the right lung
A patient who is paraplegic secondary to spinal cord transection at T3 develops bradycardia and facial flushing during a nephrectomy under general anesthesia with nitrous oxide, fentanyl, and atracurium. The most likely cause of this response is
- (A) release of histamine
- (B) stimulation of the carotid sinus
- (C) release of prostaglandins
- (D) vagal response to peritoneal traction
- (E) release of epinephrine
A 40-year-old patient has pain following injection of 8 ml of thiopental 2.5% through a right radial artery catheter. His hand remains pink. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- (A) Injection of lidocaine through the catheter
- (B) Injection of nitroglycerin through the catheter
- (C) Injection of papaverine through the catheter
- (D) Right stellate ganglion block
- (E) No intervention
In a patient with ventricular fibrillation refractory to repeated attempts at defibrillation and epinephrine administration, the most appropriate management is administration of
- (A) amiodarone
- (B) procainamide
- (C) propranolol
- (D) quinidine
- (E) verapamil
A patient with chronic paraplegia (T4 level) is undergoing cystoscopy and removal of bladder calculi without anesthesia. After 10 minutes, blood pressure is 240/100 mmHg and pulse is 50 bpm. The most appropriate management is administration of
- (A) spinal anesthesia
- (B) inhalational anesthesia
- (C) thiopental intravenously
- (D) methyldopa intravenously
- (E) nitroprusside intravenously
Which of the following perioperative interventions decreases the risk for renal insufficiency in patients undergoing aortic aneurysm repair?
- (A) Administration of furosemide
- (B) Administration of mannitol
- (C) Administration of renal-dose dopamine
- (D) Epidural anesthesia
- (E) Preoperative volume expansion
A 68-year-old man who is scheduled for outpatient cystoscopy has non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus controlled with glipizide (Glucatrol) 5 mg twice daily. He has had nothing to eat since awakening this morning and has not taken glipizide today. His blood glucose level is 185 mg/dl. Before proceeding, the most appropriate management is to administer
- (A) glipizide 5 mg orally
- (B) NPH insulin 10 units subcutaneously
- (C) regular insulin 10 units intravenously
- (D) dextrose and regular insulin by infusion
- (E) no additional diabetic medication
In a patient undergoing liver transplantation, sodium bicarbonate and calcium chloride are administered immediately before reperfusion of the transplanted liver to counteract
- (A) coagulopathy
- (B) decreased cardiac output
- (C) hyperkalemia
- (D) hypermagnesemia
- (E) hypotension
A 75-year-old man with aortic stenosis and coronary artery disease has a preinduction heart rate of 68 bpm and blood pressure of 125/70 mmHg. After induction of anesthesia with fentanyl, midazolam, and pancuronium, heart rate is 90 bpm and blood pressure is 85/45 mmHg. ECG shows a new ST-segment elevation in lead II. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management?
- (A) Ephedrine
- (B) Epinephrine
- (C) Esmolol
- (D) Nitroglycerin
- (E) Phenylephrine
Which of the following is the most effective treatment of shivering following general anesthesia?
- (A) Administration of droperidol
- (B) Administration of morphine
- (C) Administration of midazolam
- (D) Administration of warm intravenous fluids
- (E) Skin-surface warming
Ten minutes after induction of anesthesia with thiopental and isoflurane but before incision, a patient's nasopharyngeal temperature has decreased to 35.4°C. Which of the following contributed most to this decrease in temperature?
- (A) Anesthesia-induced block of nonshivering thermogenesis
- (B) Failure to use a warming blanket
- (C) Infusion of room-temperature crystalloid
- (D) Inhalation of room-temperature gases
- (E) Mixing of peripheral and central blood
A patient is bleeding excessively after routine transurethral resection of the prostate. Re-exploration discloses diffuse oozing. The most appropriate management is administration of
- (A) platelets
- (B) fresh frozen plasma
- (C) desmopressin
- (D) epsilon-aminocaproic acid
- (E) cryoprecipitate
During transurethral resection of the prostate, intravascular absorption of glycine irrigant most commonly produces
- (A) alkalosis
- (B) hemolysis
- (C) hypertension
- (D) tachycardia
- (E) wheezing
In patients with head trauma, which of the following factors results in a return of arterial pH toward normal levels after two days of mechanical hyperventilation?
- (A) Decreased renal absorption of hydrogen ions
- (B) Decreased renal blood flow
- (C) Increased PaCO2 with constant minute ventilation
- (D) Increased renal excretion of bicarbonate ions
- (E) Normalized cerebrospinal fluid pH
A 70-year-old man with mild hypertension and aortoiliac occlusive disease is undergoing aortofemoral bypass grafting. Which of the following interventions is most effective in maintaining renal perfusion during infrarenal aortic clamping?
- (A) Infusion of dopamine at 2 mcg/kg/min
- (B) Infusion of sodium nitroprusside
- (C) Intravenous administration of furosemide
- (D) Intravenous administration of mannitol
- (E) Volume loading with crystalloid
The acute onset of hypotension without a decrease in mixed venous oxygen saturation is most likely associated with the onset of
- (A) hemorrhage
- (B) myocardial infarction
- (C) pulmonary edema
- (D) pulmonary embolus
- (E) sepsis
Preoperative evaluation of a patient who has marked malnutrition will demonstrate each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) decreased respiratory muscle function
- (B) decreased serum albumin concentration
- (C) decreased metabolic rate
- (D) suppressed immune function
- (E) decreased extracellular fluid volume
Pseudocholinesterase
- (A) is increased in patients with myasthenia gravis
- (B) is inhibited by glycopyrrolate
- (C) is inhibited by pilocarpine
- (D) is synthesized by the liver
- (E) reverses atracurium blockade
The preanesthetic ECG trace (lead II) shown from a 32-year-old woman suggests
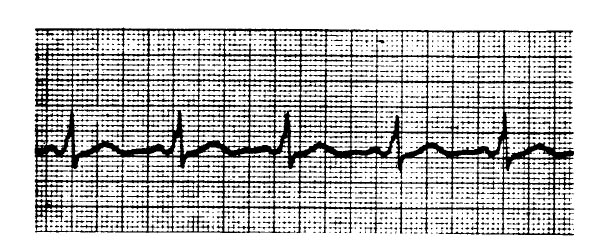
- (A) potential for tachyarrhythmia
- (B) need for preanesthetic atropine
- (C) myocardial ischemia
- (D) left bundle branch block
- (E) right ventricular hypertrophy
During right upper lobectomy and one-lung ventilation with a double-lumen endotracheal tube, the PaO2 decreases to 40 mmHg. The PaCO2 is 39 mmHg. Which of the following is most appropriate?
- (A) Confirm position of the tube with bronchoscopy
- (B) Apply 5 cmH20 continuous positive airway pressure to the nondependent lung
- (C) Apply 5 cmH20 positive end-expiratory pressure to the dependent lung
- (D) Resume two-lung ventilation
- (E) Clamp the pulmonary artery of the nondependent lung
A 36-year-old woman develops acute airway obstruction 24 hours after total thyroidectomy. The most likely cause is
- (A) bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve injury
- (B) unilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve injury
- (C) hypocalcemia
- (D) subglottic edema
- (E) tracheomalacia
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment of methemoglobinemia prior to emergency surgery?
- (A) Hydroxocobalamin
- (B) Methylene blue
- (C) Oxygen by face mask
- (D) Packed red blood cells
- (E) Thiosulfate
Which of the following results in decreased mixed venous oxygen saturation?
- (A) Cardiogenic shock
- (B) Decreased metabolic rate
- (C) Increased cardiac output
- (D) Left-to-right intracardiac shunt
- (E) Pulmonary vasodilation
If a patient with excessive bleeding during exploratory laparotomy has a normal activated clotting time, the LEAST likely cause of the bleeding is
- (A) antithrombin III deficiency
- (B) dilutional thrombocytopenia
- (C) fibrinolysis
- (D) administration of heparin 5000 units
- (E) preoperative ingestion of aspirin
A patient who is scheduled for a gastrectomy had abnormal liver function tests for four days following a prior cholecystectomy. In your consultation note, you should
- (A) recommend sevoflurane anesthesia since abnormal postoperative liver function tests are unlikely with this drug
- (B) recommend subarachnoid anesthesia since changes in hepatic blood flow would be less than with general anesthesia
- (C) indicate that abnormal liver function tests are likely to follow this operation regardless of the anesthetic drugs used
- (D) require preoperative screening for hepatitis B antigen and antibodies
- (E) recommend avoiding halothane since it is more likely to produce hepatitis in patients who had previous upper abdominal surgery
A patient has decreased lung compliance and hypoxemia after a 30-minute episode of laryngospasm following extubation. The most likely cause is
- (A) allergic reaction to the anesthetic
- (B) altered alveolar-capillary membrane permeability
- (C) anesthetic-induced lymphatic dysfunction
- (D) increased pulmonary capillary pressure
- (E) negative pulmonary interstitial hydrostatic pressure
Following a right lower lobectomy, a patient develops a bronchopleural fistula and becomes hypoxic. He is orally intubated and mechanically ventilated with pure oxygen. PaO2 is 65 mmHg, PaCO2 is 70 mmHg, and pH is 7.25. Which of the following will produce the most favorable change in the blood gases?
- (A) Increasing ventilatory frequency
- (B) Increasing suction on the chest tube
- (C) Applying 10 cmH2O positive end-expiratory pressure
- (D) Using a double-lumen tube for differential ventilation
- (E) Starting negative-pressure ventilation
A patient becomes flushed, dyspneic, and hypotensive during transfusion of 1 unit of packed red blood cells in the PACU. After discontinuing the transfusion, the most appropriate next step is administration of
- (A) aminophylline
- (B) cimetidine
- (C) diphenhydramine
- (D) epinephrine
- (E) hydrocortisone
A 28-year-old patient has severe laryngospasm after extubation of the trachea following general anesthesia. Administration of 100% oxygen using continuous positive airway pressure does not improve symptoms. SpO2 is 75%. Which of the following is the most appropriate immediate management?
- (A) Laryngeal mask airway
- (B) Lidocaine
- (C) Racemic epinephrine
- (D) Succinylcholine
- (E) Cricothyroidotomy
A patient receiving mechanical ventilation with oxygen 60% postoperatively has a PaO2 of 160 mmHg and a PaCO2 of 38 mmHg. One hour later, with mechanical ventilation unchanged, the PaO2 is 150 mmHg and PaCO2 is 48 mmHg. The most likely cause of these changes is
- (A) metabolic acidosis
- (B) pulmonary embolism
- (C) increased body temperature
- (D) interstitial pulmonary edema
- (E) aspiration pneumonia
A 70-year-old patient is shivering and has chest pain in the PACU following a cholecystectomy. Heart rate is 120 bpm, and blood pressure is 220/120 mmHg. SpO2 is 97% at an FiO2 of 0.4. An ECG shows ST-T wave changes, which are not affected by intravenous administration of nitroglycerin. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- (A) Administration of esmolol
- (B) Administration of hydralazine
- (C) Administration of nitroprusside
- (D) Application of a warming blanket
- (E) Increasing FiO2
A 36-year-old woman who undergoes peritoneal dialysis for chronic renal failure requires emergency surgical exploration for bowel obstruction. Serum creatinine concentration is 9.8 mg/dl and BUN concentration is 124 mg/dl. The most likely abnormality of coagulation is
- (A) decreased euglobulin lysis time
- (B) decreased platelet count
- (C) prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time
- (D) prolonged bleeding time
- (E) prolonged prothrombin time
Patients with acute alcohol intoxication are at increased risk for each of the following complications of general anesthesia EXCEPT
- (A) aspiration of gastric contents
- (B) hyperglycemia
- (C) hypothermia
- (D) ketoacidosis
- (E) respiratory depression
During rapid-sequence induction prior to an emergency surgical procedure, a 20-year-old patient vomits gastric contents containing particulate matter. An endotracheal tube is easily inserted and ventilation with pure oxygen is initiated. Despite the presence of bilateral breath sounds, SpO2 is 90%. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- (A) Administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics
- (B) Intravenous administration of high-dose methylprednisolone
- (C) Bronchial lavage with normal saline solution
- (D) Bronchoscopy to remove particulate matter
- (E) Cancellation of the surgical procedure
During laser excision of vocal cord polyps in a 5-year-old boy, dark smoke suddenly appears in the surgical field. The trachea is intubated and anesthesia is being maintained with halothane, nitrous oxide, and oxygen. The most appropriate initial step is to
- (A) change from oxygen and nitrous oxide to air
- (B) fill the oropharynx with water
- (C) instill water into the endotracheal tube
- (D) remove the endotracheal tube
- (E) ventilate with carbon dioxide
During isoflurane anesthesia, a 45-year-old patient with chronic asthma has wheezing, prolonged expiration, sinus tachycardia of 120 bpm, and premature ventricular contractions. Preoperative medication included cromolyn and theophylline. The most appropriate treatment is to administer
- (A) albuterol aerosol
- (B) aminophylline by intravenous infusion
- (C) cromolyn aerosol
- (D) halothane
- (E) hydrocortisone by intravenous bolus
Which of the following is the best method of pacing to improve cardiac output in a patient with third-degree heart block?
- (A) VOO
- (B) AOO
- (C) VVI
- (D) DVI
- (E) Transcutaneous
A patient with a fasting blood glucose concentration of 100 mg/dL undergoes a four-hour operation under general anesthesia without intraoperative administration of glucose. On emergence the most likely finding will be
- (A) marked hypoglycemia
- (B) mild hypoglycemia
- (C) normoglycemia
- (D) mild hyperglycemia
- (E) marked hyperglycemia
Which of the following is the LEAST likely cause of a prolonged prothrombin time?
- (A) Chronic warfarin therapy
- (B) Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- (C) Hemophilia A
- (D) Systemic heparinization
- (E) Vitamin K deficiency
A 65-year-old man is disoriented and has a headache and nausea in the recovery room 30 minutes after transurethral resection of the prostate with glycine irrigation performed under spinal anesthesia. Heart rate is 50 bpm and blood pressure is 180/110 mmHg. Which of the following is LEAST likely?
- (A) Decreased serum osmolality
- (B) Serum sodium concentration 132 mEq/L
- (C) Increased serum ammonia concentration
- (D) Bibasilar rales
- (E) Jugular venous distention
A 75-year-old man is confused, restless and disoriented two days after an aortic aneurysm repair. Serum sodium concentration is 112 mEq/L, serum osmolality is low, and urine is hypertonic. The most appropriate treatment is
- (A) restriction of fluid intake
- (B) administration of isotonic saline solution
- (C) administration of hypertonic (3%) saline solution
- (D) administration of spironolactone
- (E) infusion of mannitol 25 g
A patient is in sinus rhythm but has no pulse during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. There is marked resistance to positive pressure ventilation and breath sounds are difficult to hear bilaterally. The endotracheal tube is clearly in the trachea. The most appropriate next step in management is to
- (A) administer isoetharine by inhalation
- (B) apply electrical countershock
- (C) insert needles in the left and right chest
- (D) order a roentgenogram of the chest
- (E) start an infusion of aminophylline
Which of the following statements concerning absorption of irrigation fluid during transurethral resection of the prostate is true?
- (A) Hydrostatic pressure has minimal effect on the amount of fluid absorbed
- (B) Typically 10 to 30 ml of fluid per minute are absorbed
- (C) Use of iso-osmotic solutions decreases the risk of hyponatremia
- (D) CNS complications are independent of the type of fluid used
- (E) Spinal anesthesia to T6 will mask the symptoms of overhydration
A patient with moderate hypothyroidism and unstable angina requires urgent coronary artery bypass grafting. Which of the following is most appropriate before proceeding with the operation?
- (A) Initiation of epinephrine infusion
- (B) Intramuscular administration of a barbiturate
- (C) Intravenous administration of triiodothyronine (T3)
- (D) Intravenous administration of thyroxine (T4)
- (E) Treatment of myocardial ischemia
Which of the following findings on the left is most likely to be associated with an increased risk of complications with cannulation of the left internal jugular vein compared with cannulation of the right internal jugular vein?
- (A) Longer recurrent laryngeal nerve
- (B) Lower location of the cupola of the pleura
- (C) More acute angle between the internal jugular and innominate veins
- (D) More anterior location of the phrenic nerve
- (E) Presence of the thoracic duct
A 35-year-old woman undergoes a one-hour abdominal liposuction procedure under general anesthesia. During the procedure, 2000 ml of crystalloid is administered and 800 ml of fatty tissue is extracted. Thirty minutes postoperatively, blood pressure is 75/40 mmHg and heart rate is 100 bpm; SpO2 is 94% on room air. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
- (A) Acute systemic vasodilation
- (B) Circulating free fatty acids
- (C) Hypocalcemia
- (D) Inadequate intravascular volume replacement
- (E) Venous fat embolism
One hundred children who are to have strabismus surgery are enrolled in a research protocol. Fifty receive a new antiemetic and 50 receive a placebo preoperatively. Fifteen children in the treatment group and 37 children in the control group have nausea and vomiting postoperatively. Which of the following analyses is most appropriate for determining the statistical significance of the group differences?
- (A) Analysis of variance
- (B) Chi-square analysis
- (C) Linear regression and correlation coefficient
- (D) Student's t-test
- (E) Wilcoxon's rank sum test
Pulmonary artery occlusion pressure
- (A) does not reliably reflect left ventricular end-diastolic volume when left ventricular compliance is reduced
- (B) inaccurately reflects left atrial pressure when left atrial pressure exceeds 15 mmHg
- (C) is measured at end-inspiration in mechanically ventilated patients
- (D) overestimates left atrial pressure in patients with poor lung compliance
- (E) reflects left atrial pressure only if the catheter tip is located in zone II of the lung
Following blunt trauma to the chest, a patient has tachycardia, hypotension, and markedly distended neck veins. Each of the following is expected EXCEPT
- (A) cardiac output of 2.1 L/min
- (B) mixed venous oxygen saturation of 75%
- (C) pulmonary artery occlusion pressure of 25 mmHg
- (D) pulmonary artery diastolic pressure of 25 mmHg
- (E) right atrial pressure of 25 mmHg
Which of the following combinations of hemoglobin, blood gases, and cardiac output provides the greatest delivery of oxygen to tissue? (Hb, PaO2, SaO2, CO)
- (A) 7.0 85 95 7.0
- (B) 8.0 290 100 8.0
- (C) 9.9 61 90 9.8
- (D) 12.0 140 100 4.5
- (E) 16.0 40 75 5.8
A 50-year-old patient undergoes subtotal thyroidectomy for Graves' disease. In the immediate postoperative period, he has marked hoarseness but no stridor. The most likely cause of the hoarseness is trauma to the
- (A) external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve
- (B) internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve
- (C) recurrent laryngeal nerve
- (D) glossopharyngeal nerve
- (E) vocal cords
An endobronchial Robertshaw tube is inserted for resection of a midesophageal tumor under isoflurane, oxygen, pancuronium anesthesia. Forty minutes into a planned two-hour resection, arterial blood gas values are reported as PO2 45 mmHg, PCO2 45 mmHg, and pH 7.33. Ten minutes earlier, the values were PO2 210 mmHg, PCO2, 41 mmHg, and pH 7.39. The first action should be to
- (A) reposition the Robertshaw tube
- (B) apply positive end-expiratory pressure to the ventilated lung
- (C) reinflate and ventilate the non ventilated lung
- (D) increase minute ventilation
- (E) repeat the arterial blood gas analysis
Which of the following pre-existing conditions predisposes to new-onset third-degree heart block during pulmonary artery catheterization?
- (A) First-degree heart block
- (B) Left bundle branch block
- (C) Sick sinus syndrome
- (D) Sinus bradycardia
- (E) Wenckebach second-degree heart block
A previously healthy, 60-kg, 17-year-old boy is undergoing emergency surgery for a gunshot wound involving the iliac vein. Ventilation is controlled with a tidal volume of 700 ml/breath, rate of 10/min, and peak inspiratory pressure of 30 cmH2O. Body temperature is normal. The most likely cause of an end-tidal carbon dioxide partial pressure of 16 mmHg is
- (A) endobronchial intubation
- (B) excessive expiratory time
- (C) excessive tidal volume
- (D) low cardiac output
- (E) pulmonary aspiration
Which of the following complications is more likely to occur during cannulation of the left internal jugular vein than during cannulation of the right internal jugular vein?
- (A) Injury to the thoracic duct
- (B) Injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve
- (C) Injury to the phrenic nerve
- (D) Perforation of the esophagus
- (E) Pneumothorax
At a body temperature of 30°C, resistance to blood flow increases because of
- (A) increased hematocrit
- (B) increased plasma fibrinogen concentration
- (C) increased viscosity of blood
- (D) rouleaux formation of red blood cells
- (E) sequestration of platelets in portal circulation
Which of the following statements concerning autonomic hyperreflexia after spinal cord transection is true?
- (A) It occurs within 24 hours after the injury
- (B) It occurs with lesions below T10
- (C) It is caused by a reflex increase in parasympathetic outflow
- (D) It is characterized by paroxysmal hypotension and tachycardia
- (E) It is prevented by blocking afferent visceral pathways
A 70-kg 61-year-old patient undergoes a four-hour resection of an abdominal aortic aneurysm during anesthesia with fentanyl and enflurane. Infrarenal clamping is required during the procedure. Twelve hours after the procedure, urine output is 15 ml/hr with a fractional sodium excretion of 6%. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Enflurane nephrotoxicity
- (B) Hypovolemia
- (C) Intraoperative renal ischemia
- (D) Positive pressure ventilation
- (E) Unilateral ureteral obstruction
Administration of 200 mEq of sodium bicarbonate during cardiopulmonary resuscitation is associated with
- (A) CSF alkalosis
- (B) hypercalcemia
- (C) hypercarbia
- (D) hyperkalemia
- (E) shift of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the right
A 38-year-old woman with hyperthyroidism is undergoing open reduction and internal fixation of a fractured humerus with isoflurane anesthesia. Intraoperatively her heart rate increases to 120 bpm with occasional premature ventricular contractions. The most appropriate therapy at this time is to
- (A) discontinue isoflurane
- (B) administer edrophonium
- (C) administer esmolol
- (D) administer lidocaine
- (E) administer propylthiouracil
A 30-year-old woman is undergoing laparoscopic tubal ligation. Thirty minutes after induction of general anesthesia, arterial oxygen saturation has decreased to 89%. Arterial blood gases at an FiO2 of 1.0 are PaO2 63 mmHg and PaCO2 40 mmHg; PetCO2 is 32 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Carbon dioxide embolus
- (B) Endobronchial intubation
- (C) Hypoventilation
- (D) Inadvertent application of high levels of positive end-expiratory pressure
- (E) Leak in the capnography sampling catheter
During laser excision of a vocal cord polyp, the tracheal tube ignites. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- (A) Continue ventilation with air
- (B) Ensure patency of the endotracheal tube
- (C) Extubate the trachea
- (D) Flood the surgical field with saline solution
- (E) Increase the concentration of nitrous oxide
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- (A) is inactivated by irradiation
- (B) is transmitted by cryoprecipitate
- (C) is transmitted by 5% albumin
- (D) passes through intact dermis
- (E) provokes an immediate antibody response
During acute normovolemic hemodilution in an adult, which of the following compensatory mechanisms is most important in maintaining tissue oxygenation?
- (A) Increased cardiac output
- (B) Increased oxygen extraction
- (C) Increased synthesis of erythropoietin
- (D) Redistribution of regional blood flow
- (E) Shift of the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve
Intraoperative heat loss in an unclothed, undraped patient is caused primarily by
- (A) conduction to colder objects
- (B) convective heat loss
- (C) insensible perspiration
- (D) radiant heat loss to the environment
- (E) respiratory tract water loss
Unilateral or bilateral diaphragmatic paralysis is a complication of each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) surgical ligation of a patent ductus arteriosus
- (B) use of pericardial ice-slush for topical cardiac hypothermia
- (C) stellate ganglion block
- (D) interscalene brachial plexus block
- (E) C6 cervical fracture-dislocation
During insufflation of the peritoneal cavity with carbon dioxide at the start of laparoscopy, heart rate increases to 140 bpm, blood pressure decreases to 70/40 mmHg, and a loud murmur is heard through the esophageal stethoscope. The most appropriate immediate step is to
- (A) administer a vasoconstrictor
- (B) infuse crystalloid solution rapidly
- (C) discontinue the inhaled anesthetic
- (D) insert a central venous catheter
- (E) deflate the abdomen
During general anesthesia, a patient has the acute onset of atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and hypotension to 50 mmHg systolic. The most appropriate treatment is
- (A) cardioversion
- (B) digoxin
- (C) esmolol
- (D) ouabain
- (E) verapamil
Which of the following physiologic changes occurs with immersion in water during extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy?
- (A) Decreased cardiac output
- (B) Decreased central venous pressure
- (C) Increased expiratory reserve volume
- (D) Increased functional residual capacity
- (E) Increased stroke volume
A previously healthy 28-year-old woman scheduled for laparoscopic tubal ligation becomes, agitated and refuses to undergo the procedure after being brought to the operating room. This behavior most likely resulted from preoperative administration of
- (A) droperidol
- (B) cimetidine
- (C) atropine
- (D) meperidine
- (E) midazolam
A 57-year-old man has back pain, a heart rate of 90 bpm, decreased pulse in the left arm, and blood pressure of 200/110 mmHg. During infusion of nitroprusside, heart rate increases to 115 bpm and blood pressure decreases to 140/80 mmHg. The most appropriate management at this time is administration of
- (A) droperidol
- (B) nifedipine
- (C) normal saline solution
- (D) propranolol
- (E) verapamil
The primary purpose of denitrogenation prior to anesthetic induction is to
- (A) blunt hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
- (B) improve ventilation and perfusion matching
- (C) increase contribution of second gas effect to rate of induction
- (D) increase oxygen reserve in the functional residual capacity
- (E) maximize arterial oxygen content
Which of the following findings is most likely in patients with acute transection of the spinal cord at the level of C6?
- (A) Autonomic hyperreflexia
- (B) Hyperkalemia with administration of succinylcholine
- (C) Hypotension
- (D) Increased pulmonary blood flow
- (E) Tachycardia
Which of the following is the most common initial manifestation of malignant hyperthermia?
- (A) Hyperkalemia
- (B) Increased distal esophageal temperature
- (C) Increased PETCO2
- (D) Red discoloration of urine
- (E) Ventricular irritability
A 70-kg 78-year-old man undergoing small-bowel resection during anesthesia with isoflurane in oxygen becomes hypotensive and develops frothy pink sputum in the endotracheal tube. Heart rate is 50 bpm, blood pressure is 75/60 mmHg, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure is 22 mmHg, and cardiac output is 1.7 L/min. The most appropriate initial step in management is administration of which of the following?
- (A) Albumin
- (B) Digoxin
- (C) Dopamine
- (D) Esmolol
- (E) Nitroglycerin
Each of the following would be expected in an otherwise healthy 165-kg woman undergoing cholecystectomy EXCEPT
- (A) decreased functional residual capacity
- (B) decreased ventilatory response to carbon dioxide
- (C) increased cardiac output
- (D) increased gastric fluid volume
- (E) increased metabolism of volatile anesthetics
A 30-year-old, 70-kg woman with mitral stenosis is scheduled for elective laparoscopic sterilization. Preoperatively she is taking digoxin and an unknown medication for chronic mental depression. The EKG demonstrates atrial fibrillation. Heart rate is 68 bpm. Anesthesia is induced with thiopental followed by nitrous oxide 50%, halothane 0.75%, and a continuous succinylcholine infusion. The ventilator is set to deliver a minute volume of 5 liters through an endotracheal tube. As the carbon dioxide is being insufflated into the abdomen, the blood pressure is noted to be elevated (150/100 mmHg) and ventricular bigeminy is present. The most appropriate therapy is to
- (A) increase the halothane concentration to 1.25%
- (B) discontinue the succinylcholine infusion
- (C) increase minute ventilation to 7.5 L/min
- (D) administer potassium 5 mEq intravenously over one minute followed by propranolol 0.25 mg
- (E) measure arterial blood gas and serum electrolyte values
During induction of anesthesia in a 70-year-old man with aortic stenosis, the blood pressure decreases from 140/ 80 to 70/45 mmHg as the cardiac rhythm changes from normal sinus at 70 bpm to junctional at 120 bpm. The most appropriate initial therapy would be
- (A) cardioversion
- (B) esmolol
- (C) fluid bolus
- (D) phenylephrine
- (E) verapamil
A patient develops jaundice one week after undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy during halothane anesthesia. Laboratory studies show an increased serum alkaline phosphatase concentration, a mildly increased serum aspartate aminotransferase concentration, and a markedly increased conjugated bilirubin fraction. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- (A) Biliary obstruction
- (B) Gilbert's disease
- (C) Halothane-associated hepatitis
- (D) Hematoma resorption
- (E) Infectious hepatitis
Hypomagnesemia is associated with
- (A) decreased risk for digitalis toxicity
- (B) dysrhythmias sensitive to bretylium
- (C) hypercalcemia
- (D) prolonged succinylcholine blockade
- (E) surgery requiring cardiopulmonary bypass
Which of the following factors is LEAST predictive of postoperative cardiac complications?
- (A) Congestive heart failure
- (B) Major vascular surgery
- (C) Premature ventricular contractions
- (D) Preoperative hypertension
- (E) Recent myocardial infarction
A patient with alcoholic cirrhosis, ascites, and gastrointestinal bleeding receives 4 units of red blood cells prior to anesthesia with isoflurane in oxygen for emergency exploratory laparotomy. After the peritoneum is opened and the fluid is drained, blood pressure decreases to 60/40 mmHg and SpO2 decreases to 90%. The most likely cause of the hypoxemia is
- (A) acute myocardial ischemia
- (B) decreased 2,3-diphosphoglycerate in transfused blood
- (C) increased intrapulmonary shunting
- (D) relative hypovolemia
- (E) venous air embolism
Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management of a patient with hypotension secondary to sepsis?
- (A) Calcium chloride
- (B) Corticosteroids
- (C) Crystalloid infusion
- (D) Dopamine
- (E) Fresh frozen plasma
A patient has hoarseness after undergoing surgery involving the aortic arch. The most likely cause is an injury to which of the following nerves?
- (A) Glossopharyngeal
- (B) Left recurrent laryngeal
- (C) Right recurrent laryngeal
- (D) Left superior laryngeal
- (E) Right superior laryngeal
An EKG shows ventricular tachycardia in a patient with a heart rate of 160 bpm and a blood pressure of 90/60 mmHg. The best initial therapeutic maneuver prior to cardioversion is
- (A) carotid sinus massage
- (B) intravenous administration of bretylium
- (C) intravenous administration of amiodarone
- (D) intravenous administration of propranolol
- (E) precordial "thump"
A 70-kg, 50-year-old man is scheduled for muscle flap closure of a decubitus ulcer over the sacrum. He has been quadriplegic at the level of C6-7 for six years. Which of the following is most likely to result from subarachnoid anesthesia with tetracaine 10 mg for this procedure?
- (A) Atrioventricular block
- (B) Decreased risk for autonomic dysreflexia
- (C) Impaired expiratory muscle function
- (D) Impaired inspiratory muscle function
- (E) Inadequate block of spastic movements
Statistical analysis of 20 patients shows a mean cardiac output (CO) of 5 L/min with a standard deviation of 1 L/min. The distribution pattern in the sample population is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate conclusion?
- (A) Approximately 33% of the sample population would be expected to have a CO between 4 and 6 L/min
- (B) Approximately 95% of the sample population would be expected to have a CO between 3 and 7 L/min
- (C) Ten of the sample patients have a cardiac output greater than 5 L/min
- (D) The mean and the median are both at the 50th percentile
- (E) The median and the mode are the same in the sample population
A 45-year-old patient with chronic alcoholism develops jaundice four days after a cholecystectomy under halothane/morphine general anesthesia. Bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase are elevated, but ALT is only slightly above normal. All values were within normal limits preoperatively. The most likely cause of jaundice is
- (A) opioid-induced spasm of the sphincter of Oddi
- (B) hepatic dysfunction secondary to halothane exposure
- (C) worsening of underlying chronic hepatitis
- (D) extrahepatic biliary obstruction
- (E) acute viral hepatitis
DC shocks of 200 joules applied directly to the heart are likely to
- (A) worsen coronary perfusion
- (B) prevent postshock arrhythmias
- (C) produce myocardial contractile abnormalities
- (D) increase myocardial impedance
- (E) decrease myocardial temperature
Each of the following structures may participate in causing acute bradycardia during strabismus surgery EXCEPT the
- (A) globe
- (B) rectus muscles
- (C) optic nerve
- (D) trigeminal nerve
- (E) vagus nerve
Which of the following complications is the primary cause of neurologic deficit following carotid endarterectomy?
- (A) Global hypoperfusion
- (B) Hypertension
- (C) Hypotension
- (D) Improper shunt insertion
- (E) Thromboembolism
Which of the following processes is primarily responsible for the decrease in core body temperature that occurs during the first hour of general anesthesia?
- (A) Decreased production of heat
- (B) Convective heat loss caused by cutaneous vasodilation
- (C) Evaporative heat loss during skin preparation
- (D) Heat loss from the respiratory tract
- (E) Redistribution of core body heat to the periphery
Which of the following is the best initial treatment of anaphylaxis that occurs during general anesthesia?
- (A) Diphenhydramine
- (B) Dopamine
- (C) Epinephrine
- (D) Hydrocortisone
- (E) Ranitidine
Which of the following statements best describes testing for susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia (MH)?
- (A) Live skeletal muscle cells are required for testing
- (B) The MH gene is located on the X chromosome
- (C) Muscle biopsy is appropriate in children younger than 1 year
- (D) A normal serum creatine phosphokinase concentration eliminates the need for muscle biopsy
- (E) Succinylcholine is used to stimulate muscle obtained on biopsy for MH
A patient has a decrease in heart rate from 80 to 50 bpm and a decrease in blood pressure from 140/90 to 60/40 mmHg while in the recovery room after adrenalectomy for pheochromocytoma. The most appropriate treatment is administration of
- (A) atropine
- (B) calcium
- (C) hydrocortisone
- (D) isoproterenol
- (E) norepinephrine
Each of the following improves coagulation in patients with uremia EXCEPT
- (A) conjugated estrogens
- (B) desmopressin
- (C) dialysis
- (D) epsilon-aminocaproic acid
- (E) platelet transfusion
Which of the following is the most likely effect of infrarenal cross clamping of the aorta without pharmacologic manipulation?
- (A) Decreased cardiac output
- (B) Decreased pulmonary artery occlusion pressure
- (C) Increased left ventricular stroke volume
- (D) Increased renal blood flow
- (E) Improved myocardial oxygen supply-demand ratio
A 57-year-old man has back pain, a heart rate of 90 bpm, decreased pulse in the left arm, and blood pressure of 200/110 mmHg. During infusion of nitroprusside, heart rate increases to 115 bpm and blood pressure decreases to 140/80 mmHg. The most appropriate management at this time is administration of
- (A) droperidol
- (B) nifedipine
- (C) normal saline solution
- (D) propranolol
- (E) verapamil
Left ventricular subendocardial perfusion pressure is best estimated by the difference between
- (A) mean arterial and central venous pressures
- (B) diastolic arterial and pulmonary artery occlusion pressures
- (C) mean arterial and pulmonary artery occlusion pressures
- (D) systolic arterial and pulmonary artery occlusion pressures
- (E) diastolic arterial and central venous pressures