250 questions match your search.
A 60-kg, 38-year-old woman undergoes laparoscopic tubal ligation. Paralysis is maintained for one hour with infusion of succinylcholine at a rate of 10 mg/min. At the end of the procedure, respirations are shallow and tetanic fade is noted on neuromuscular stimulation. In addition to continued mechanical ventilation, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- (A) Observe until the patient recovers spontaneously
- (B) Monitor until PetC02 reaches 50 mmHg
- (C) Determine dibucaine number
- (D) Administer fresh frozen plasma
- (E) Administer glycopyrrolate and neostigmine
Severe nausea and vomiting in the PACU is most effectively treated with a drug that acts as an antagonist at which of the following receptors?
- (A) Alpha-adrenergic
- (B) Beta-adrenergic
- (C) Dopamine
- (D) GABA
- (E) Glutamate
A 66-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease who underwent colectomy 12 hours ago has been receiving an epidural infusion of fentanyl at a rate of 100 mcg/hr. Which of the following is LEAST likely to develop?
- (A) Hypotension
- (B) Nausea
- (C) Pruritus
- (D) Respiratory depression
- (E) Urinary retention
The low fetal/maternal plasma ratio of bupivacaine compared with lidocaine is due to
- (A) fetal tissue binding
- (B) fetal plasma protein binding
- (C) maternal plasma protein binding
- (D) ionization in maternal blood
- (E) ionization in fetal blood
Normal pseudocholinesterase
- (A) is highly concentrated at the motor end-plate
- (B) hydrolyzes succinylcholine by Hofmann elimination
- (C) is produced primarily at nerve terminals
- (D) is antagonized by acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
- (E) resists dibucaine inhibition more than its atypical variant
The hemodynamic changes shown would most likely result from infusion of
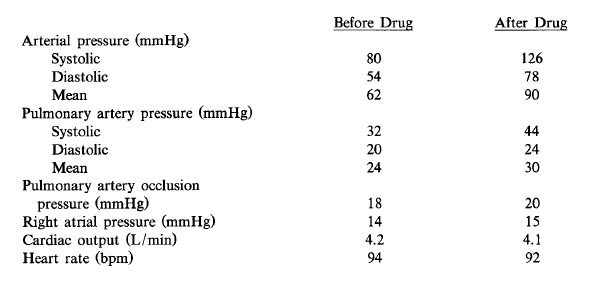
- (A) dopamine
- (B) epinepherine
- (C) dobutamine
- (D) norepinepherine
- (E) isoproterenol
During recovery from halothane anesthesia, an alveolar concentration of 0.1% will have the greatest effect on
- (A) myocardial contractility
- (B) ventilatory response to hypercarbia
- (C) atrioventricular conduction
- (D) ventilatory response to hypoxia
- (E) neuromuscular transmission
Which of the following is a sign of cyclosporine toxicity?
- (A) Abnormal hepatic enzyme activity
- (B) Decreased hemoglobin concentration
- (C) Increased serum creatinine concentration
- (D) Nodular density on radiograph of the chest
- (E) ST-T wave changes on ECG
A 35-year-old woman with a grade III subarachnoid hemorrhage is undergoing clipping of a middle cerebral artery aneurysm 48 hours after initial hemorrhage. Which of the following drugs used to induce hypotension is LEAST likely to affect intracranial pressure?
- (A) Esmolol
- (B) Hydralazine
- (C) Isoflurane
- (D) Nitroglycerin
- (E) Sodium nitroprusside
Neostigmine administered intravenously without atropine can produce each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) arousal
- (B) bradycardia
- (C) bronchoconstriction
- (D) increased gastric motility
- (E) increased urinary bladder tone
Which of the following findings is most likely in patients receiving intravenous milrinone?
- (A) Decreased left ventricular afterload
- (B) Decreased myocardial oxygen consumption
- (C) Increased atrioventricular conduction
- (D) Increased right ventricular preload
- (E) Stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors
Compared with thiopental, methohexital is characterized by
- (A) better absorption after rectal administration
- (B) greater protein binding
- (C) greater hepatic clearance
- (D) larger volume of distribution
- (E) more complete biotransformation
Intrabiliary pressure will be increased to the greatest extent by intravenous administration of
- (A) atropine
- (B) glucagon
- (C) naloxone
- (D) fentanyl
- (E) butorphanol
Alveolar and inspired anesthetic concentrations equilibrate more rapidly with nitrous oxide than with desflurane because nitrous oxide
- (A) has a higher vapor pressure
- (B) has a lower blood gas solubility
- (C) has a lower MAC
- (D) is delivered at a higher inspired concentration
- (E) produces a second gas effect
The effect of neomycin at the neuromuscular junction is
- (A) decreased by depolarizing relaxants
- (B) partially reversed by calcium
- (C) potentiated by anticholinesterases
- (D) prevented by pretreatment with magnesium
- (E) primarily prejunctional
A newly developed inhalational anesthetic has a blood-gas partition coefficient of 0.2. Which of the following statements best describes this drug compared with isoflurane?
- (A) MAC is lower
- (B) The difference between Fa and Fl during maintenance of anesthesia is greater
- (C) Time to emergence is shorter
- (D) Rapid induction requires greater overpressure
- (E) Equilibrium in a circle system with the same flow of fresh gas is slower
A patient receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy for depression undergoes an emergency cholecystectomy. Which of the following is the best means of providing postoperative analgesia in this patient?
- (A) Epidural analgesia using 0.25% bupivacaine
- (B) Intravenous meperidine
- (C) Epidural analgesia using meperidine
- (D) Epidural analgesia using 1% lidocaine with epinephrine
- (E) Intercostal analgesia using 1% lidocaine with epinephrine
Which of the following statements about thiopental is true?
- (A) Rapid uptake into maternal tissues limits its transfer to the fetus
- (B) Its short duration of action is due to its extensive binding to plasma proteins
- (C) Accumulation in fat leads to acute tolerance
- (D) Alkalinity of solution causes respiratory depression
- (E) Uptake into brain is slowed by respiratory acidosis
Miosis, incontinence, excess salivation, and convulsions are toxic effects of
- (A) amphetamines
- (B) phenothiazines
- (C) cocaine
- (D) tricyclic antidepressants
- (E) organophosphate insecticides
Each of the following affects the induction dose of thiopental EXCEPT
- (A) acute ethanol intoxication
- (B) chronic use of barbiturates
- (C) intravascular volume
- (D) rate of hepatic extraction of thiopental
- (E) serum albumin concentration
Prilocaine is NOT recommended for obstetric regional anesthesia because it
- (A) causes fetal methemoglobinemia
- (B) has a very short duration of action
- (C) is not metabolized by the newborn
- (D) is the most toxic of the amide local anesthetics
- (E) produces a longer motor block than sensory block
Each of the following statements concerning norepinephrine is true EXCEPT:
- (A) Extraneuronal uptake is important in the termination of its activity
- (B) It is formed from dopamine
- (C) Its release is facilitated by ephedrine
- (D) Its uptake is affected by cocaine
- (E) It has minimal beta2-adrenergic activity
A 25-year-old man requires exploratory laparotomy following a motor vehicle accident. He is acutely intoxicated with alcohol. Which of the following is the most likely result of the alcohol ingestion?
- (A) Hyperdynamic circulation
- (B) Hyperglycemia
- (C) Hyperthermia
- (D) Increased respiratory depression from opioids
- (E) Increased sensitivity to neuromuscular blocking drugs
Compared with isoflurane, desflurane
- (A) causes higher plasma norepinephrine levels
- (B) has greater biodegradability
- (C) has a higher blood/gas partition coefficient
- (D) has a lower MAC value
- (E) has a lower vapor pressure
The second gas effect refers to
- (A) acceleration of rise in alveolar concentration of a gas caused by concomitantly administered nitrous oxide
- (B) change in volatile anesthetic vaporizer output with the addition of nitrous oxide to the carrier gas mixture
- (C) decrease in MAC of a volatile anesthetic by addition of nitrous oxide
- (D) expansion of gas-containing spaces by addition of nitrous oxide
- (E) rapid diffusion of nitrous oxide from pulmonary capillary blood into alveolar gas at the termination of anesthesia
Awakening after a single dose of thiopental is caused by redistribution from the brain primarily to which of the following sites?
- (A) Fat
- (B) Heart
- (C) Liver
- (D) Lung
- (E) Skeletal muscle
Compared with the response of a normal patient, administration of a bolus dose of pancuronium (0.15 mg/kg) to a patient with cirrhosis and ascites would be associated with
- (A) longer duration
- (B) more rapid onset
- (C) more intense block
- (D) more difficult reversibility
- (E) similar pharmacokinetics
Ninety minutes after administration of succinylcholine 1 mg/kg to a 28-year-old woman, the train-of-four shows a T4:T1 ratio of 25%. This is most consistent with
- (A) dibucaine number of 30
- (B) hypersensitivity to succinylmonocholine
- (C) pregnancy
- (D) pretreatment with pancuronium 2 mg
- (E) severe cirrhosis
Which of the following drugs exerts a vasoconstrictor effect by blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine at the neuronal synapse?
- (A) Cocaine
- (B) Dopamine
- (C) Ephedrine
- (D) Metaraminol
- (E) Phenylephrine
During induction of anesthesia for cesarean delivery, pancuronium is inadvertently substituted for succinylcholine. The neonate shows no clinical signs of muscle relaxation because pancuronium is
- (A) highly ionized
- (B) highly protein bound
- (C) a large molecule
- (D) lipid soluble
- (E) unaffected by "ion trapping"
The physiologic function most likely to be spared when a local anesthetic differential nerve block is administered is
- (A) sweating
- (B) temperature sensation
- (C) proprioception
- (D) touch sensation
- (E) pain sensation
Which of the following limits the use of nalbuphine for relief of postoperative pain?
- (A) High incidence of nausea and vomiting
- (B) High incidence of delayed respiratory depression
- (C) Potential for inducing seizures with repeated doses
- (D) Relatively low maximal analgesic effect
- (E) Short duration of action
Which of the following drugs increases cerebral blood flow while decreasing cerebral metabolic rate?
- (A) Etomidate
- (B) Fentanyl
- (C) Isoflurane
- (D) Lidocaine
- (E) Midazolam
A 68-year-old man who is scheduled for outpatient cystoscopy has non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus controlled with glipizide (Glucatrol) 5 mg twice daily. He has had nothing to eat since awakening this morning and has not taken glipizide today. His blood glucose level is 185 mg/dl. Before proceeding, the most appropriate management is to administer
- (A) glipizide 5 mg orally
- (B) NPH insulin 10 units subcutaneously
- (C) regular insulin 10 units intravenously
- (D) dextrose and regular insulin by infusion
- (E) no additional diabetic medication
Which of the effects of epidural morphine is most resistant to intravenous naloxone?
- (A) Analgesia
- (B) Nausea
- (C) Pruritus
- (D) Respiratory depression
- (E) Urinary retention
Following antagonism of a nondepolarizing muscle relaxant with neostigmine, twitch height is normal. To achieve this effect, the percentage of the acetylcholine receptor pool that must be free of muscle relaxant is
- (A) 10
- (B) 25
- (C) 33
- (D) 50
- (E) 75
A 65-year-old patient receiving long-term clonidine therapy fails to take it one day before surgery. This would most likely
- (A) be beneficial, since clonidine decreases cardiac output
- (B) be of no consequence due to the long half-life of clonidine
- (C) produce a lower anesthetic requirement than if the drug had been continued
- (D) produce rebound hypertension
- (E) result in seizure activity
The concentration of bupivacaine is higher in maternal blood than in fetal blood because
- (A) bupivacaine is metabolized in the placenta
- (B) maternal blood has a higher pH
- (C) maternal blood has greater plasma protein binding
- (D) maternal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for bupivacaine
- (E) placental transfer of bupivacaine is limited
A 45-year-old man is scheduled for exploratory laparotomy. Six months ago, he received doxorubicin (Adriamycin) therapy for testicular cancer. This patient is at increased risk for
- (A) abnormal liver function
- (B) bone marrow depression
- (C) heart failure
- (D) chronic renal failure
- (E) pulmonary fibrosis
Which of the following statements concerning neuroleptic malignant syndrome is true?
- (A) It does not respond to dantrolene therapy
- (B) It is inherited as an autosomal trait
- (C) It is not triggered by succinylcholine
- (D) It occurs after long-term use of L-dopa
- (E) The halothane-caffeine contracture test is negative in susceptible patients
In normal tissue, which property of drugs has the greatest effect on the speed of onset of a local anesthetic?
- (A) Amide structure
- (B) Degree of protein binding
- (C) Intrinsic vasoconstrictor activity
- (D) pKa
- (E) Potency
One week after sustaining third-degree burns over 40% of his body surface area, a patient requires general anesthesia for debridement and skin grafting. Which of the following responses to neuromuscular blockers is most likely?
- (A) Clinically insignificant increases in serum potassium concentration after administration of succinylcholine 1 mg/kg
- (B) Increased risk of hyperkalemia after administration of succinylcholine 1 mg/kg
- (C) Increased sensitivity to vecuronium
- (D) Laudanosine toxicity after administration of atracurium 0.4 mg/kg
- (E) Normal serum potassium concentration if administration of succinylcholine is preceded by d-tubocurarine 3 mg
Each of the following drugs increases the duration of succinylcholine action EXCEPT
- (A) echothiophate
- (B) gentamicin
- (C) magnesium sulfate
- (D) pyridostigmine
- (E) trimethaphan
In a patient who is to undergo clipping of a cerebral aneurysm, an advantage of isoflurane over nitroprusside for induction of hypotension is
- (A) better maintenance of cardiac output
- (B) better maintenance of cerebral blood flow
- (C) greater decrease in cerebral oxygen consumption
- (D) greater decrease in afterload
- (E) more rapid titration of systemic blood pressure
Which of the following must be considered during perioperative management of a patient on long-term lithium therapy?
- (A) Intravenous fluids should include sodium
- (B) Therapy should be discontinued for 14 days prior to anesthesia
- (C) The requirement for succinylcholine is increased
- (D) The requirement for volatile anesthetics is increased
- (E) Urine output should be maintained with furosemide
Compared with thiopental, etomidate causes
- (A) greater histamine release
- (B) greater myocardial depression
- (C) greater myoclonic activity
- (D) increased seizure threshold
- (E) less nausea
A 40-year-old woman receives alfentanil 75 mcg/kg followed by an infusion of 1.5 mcg/kg/min for a one-hour cholecystectomy and cholangiogram. This regimen could be associated with each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) muscle rigidity
- (B) increased biliary tract pressure
- (C) inadequate anesthesia
- (D) postoperative respiratory depression
- (E) two to four hours of postoperative analgesia
A previously healthy 46-year-old woman has severe substernal chest pain one hour after receiving morphine sulfate 10 mg intramuscularly for an elective cholecystectomy. Vital signs, SpO2, and findings on a five-lead ECG on the operating room monitor are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- (A) Sublingual administration of nitroglycerin
- (B) Intravenous administration of butorphanol
- (C) Intravenous administration of naloxone
- (D) Cardiology consultation
- (E) Cancellation of surgery
The need for increased doses of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants in patients with extensive burns is best explained by
- (A) increased protein binding
- (B) hypermetabolism
- (C) increased glomerular filtration rate
- (D) proliferation of receptors on burned muscle
- (E) decreased volume of distribution
Which of the following characteristics of local anesthetics is associated with long duration of action?
- (A) High degree of lipid solubility
- (B) High degree of protein binding
- (C) High molecular weight
- (D) High pKa
- (E) Presence of ester linkage
Which of the following is a side effect of beta-adrenergic blockade?
- (A) Cerebral vasodilation
- (B) Decreased left ventricular filling pressures
- (C) Hypokalemia
- (D) Increased airway resistance
- (E) Uterine relaxation
Compared with a patient without liver disease, a patient with cirrhosis will have
- (A) greater accumulation of vecuronium with infusion
- (B) increased unbound plasma vecuronium concentration
- (C) more frequent occurrence of phase II block after succinylcholine administration
- (D) prolonged elimination half-life of atracurium
- (E) unchanged volume of distribution for pancuronium
The effect of succinylcholine is terminated at postsynaptic effector cells by
- (A) binding and uptake by effector cells
- (B) diffusion into capillaries
- (C) hydrolysis by junctional cholinesterase
- (D) hydrolysis by pseudocholinesterase
- (E) spontaneous degradation to succinylmonocholine
Which of the following is an effect of acetazolamide?
- (A) Glucose intolerance
- (B) Increased minute ventilation
- (C) Metabolic alkalosis
- (D) Sinus bradycardia
- (E) Slowed intravenous anesthetic induction
The correlation between anesthetic potency and lipid solubility
- (A) suggests that the number of molecules dissolved at the site of action causes anesthesia
- (B) applies to anesthetic agents dissolved in olive oil
- (C) suggests that the type of molecule causes anesthesia
- (D) is consistent with the synergistic effect of anesthetics
- (E) is not consistent with a unitary molecular site of action of anesthetics
A 100-kg, 42-year-old woman received enflurane and oxygen for clipping of an intracranial aneurysm lasting eight hours. In the first two postoperative hours, urine output is 2 liters. Serum sodium concentration is 152 mEq/L. Urine osmolality and central venous pressure are low. Which of the following is best used to establish the diagnosis?
- (A) Pulmonary artery occlusion pressure
- (B) Serum fluoride concentration
- (C) Serum osmolality
- (D) Response to antidiuretic hormone
- (E) Response to fluid restriction
Compared with midazolam, diazepam has which of the following characteristics?
- (A) Greater solubility in water
- (B) Shorter beta half-life
- (C) More potent ventilatory depressant effect
- (D) Lower risk for thrombophlebitis
- (E) A pharmacologically active metabolite
Long-term use of cimetidine is associated with
- (A) delayed emergence after thiopental induction
- (B) increased hypotension after morphine
- (C) increased risk for isoflurane-induced nephrotoxicity
- (D) prolonged action of succinylcholine
- (E) prolonged sedation with diazepam
Which of the following statements is true concerning administration of 70% nitrous oxide to a patient with an unrecognized pneumothorax?
- (A) Expansion of the pneumothorax by nitrous oxide occurs at a greater rate than expansion of bowel gas
- (B) Expansion of the pneumothorax by nitrous oxide occurs at a linear rate
- (C) The maximum expansion of a closed space occurs within 15 minutes
- (D) The maximum concentration of nitrous oxide achievable within the pneumothorax is 35%
- (E) The maximum increase in a closed gas-containing space is 100%
Which of the following is decreased by alkalinization of a 1.5% lidocaine solution?
- (A) Concentration of free base
- (B) Dose required for anesthesia
- (C) Duration of anesthesia
- (D) Intracellular concentration of ionized lidocaine
- (E) Time to onset of anesthesia
During anesthesia with nitrous oxide 65% in oxygen, fentanyl, and pancuronium, nitroprusside is administered to decrease arterial pressure to 85/50 mmHg. A decrease in PaO2 from 120 to 65 mmHg is most likely caused by
- (A) cyanide toxicity
- (B) depressed cardiac output
- (C) mild hypercarbia
- (D) metabolic acidosis
- (E) pulmonary vasodilation
In a patient who has undergone cholecystectomy, which of the following is the most likely pulmonary effect of systemically administered opioids?
- (A) Decreased Qs/Qt
- (B) Decreased dead space
- (C) Restored vital capacity
- (D) Restored functional residual capacity
- (E) Shift of the carbon dioxide response curve to the right
Which of the following is a respiratory effect of 1 MAC halothane?
- (A) Decreased contribution of abdominal muscles to exhalation
- (B) Decreased contribution of the chest wall to ventilation
- (C) Decreased respiratory rate
- (D) Decreased ratio of dead space to tidal volume
- (E) Increased tidal volume
Which of the following premedicant drug combinations is most effective in preventing passive regurgitation during anesthesia?
- (A) Cimetidine and glycopyrrolate
- (B) Metoclopramide and atropine
- (C) Metoclopramide and ranitidine
- (D) Metoclopramide, atropine, and ranitidine
- (E) Metoclopramide and sodium bicitrate
Halothane anesthesia is usually associated with an increase in
- (A) cardiac contractility
- (B) venous capacitance
- (C) arterial pressure
- (D) venous return
- (E) heart rate
A patient has severe pain after total knee arthroplasty. Systemic opioids are most likely to modify the pain through action at which of the following sites?
- (A) Corpus callosum
- (B) Hippocampus
- (C) Substantia gelatinosa
- (D) Substantia nigra
- (E) Ventral horn of the spinal cord
Hyperkalemia in response to the administration of an intubating dose of succinylcholine is associated with each of the following disorders EXCEPT
- (A) poliomyelitis
- (B) multiple sclerosis
- (C) hemiplegia
- (D) acute cervical cord transection
- (E) familial periodic paralysis
To predict the requirement for isoflurane in milliliters of vapor per minute during closed circuit anesthesia, each of the following is necessary EXCEPT
- (A) cardiac output
- (B) oxygen consumption
- (C) MAC of isoflurane
- (D) duration of administration
- (E) blood-gas partition coefficient
During nitrous oxide anesthesia, which of the following expands most rapidly?
- (A) Air bubble in the blood
- (B) Air in the intestine
- (C) Endotracheal tube cuff
- (D) Pneumothorax
- (E) Sulfahexafluoride bubble in the vitreal cavity
During therapy for eclampsia, toxic blood levels of magnesium sulfate can be distinguished from therapeutic levels by the presence of
- (A) diminished knee jerk reflex
- (B) a widened QRS complex on EKG
- (C) fetal tachycardia
- (D) maternal drowsiness
- (E) uterine rigidity
A 40-year-old man requires brief surgical relaxation after administration of neostigmine and glycopyrrolate for reversal of vecuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade. Succinylcholine 1 mg/kg is administered intravenously. Compared with a patient who has not had prior reversal of neuromuscular blockade, which of the following characterizes the succinylcholine blockade in this patient?
- (A) Greater antagonism with calcium chloride
- (B) Slower onset
- (C) Less profound
- (D) Less likelihood of phase II neuromuscular blockade
- (E) Prolonged duration
The metabolism of which of the following hypotensive agents is most likely to be affected in patients with severe renal disease?
- (A) Esmolol
- (B) Hydralazine
- (C) Nitroglycerin
- (D) Nitroprusside
- (E) Trimethaphan
During induction of anesthesia in a 70-year-old man with aortic stenosis, the blood pressure decreases from 140/ 80 to 70/45 mmHg as the cardiac rhythm changes from normal sinus at 70 bpm to junctional at 120 bpm. The most appropriate initial therapy would be
- (A) cardioversion
- (B) esmolol
- (C) fluid bolus
- (D) phenylephrine
- (E) verapamil
During pulmonary artery catheterization, a 65-year-old man receives morphine 6 mg and scopolamine 0.4 mg intravenously. The pulse oximeter indicates desaturation, which quickly resolves with stimulation. When the drapes are removed, he has unilateral eye pain, decreased visual acuity, and dilated and irregular pupils. These eye symptoms are most likely caused by
- (A) retinal hemorrhage
- (B) morphine-induced oculogyric crisis
- (C) corneal abrasion
- (D) carotid artery embolization
- (E) angle-closure glaucoma
The decreased duration of action of an intravenous dose of fentanyl compared with an intravenous dose of morphine is best explained by
- (A) greater lipid solubility
- (B) increased hepatic metabolism
- (C) less protein binding
- (D) shorter elimination half-life
- (E) smaller volume of distribution
A patient with end-stage renal disease has prolonged ventilatory depression after administration of morphine. The most likely cause is increased
- (A) serum concentration of morphine-6-glucuronide
- (B) elimination half-life of morphine
- (C) opioid receptors
- (D) receptor affinity
- (E) volume of distribution
A 70-kg patient experiences pain on incision of a thigh abscess. The area around the abscess had been infiltrated with 30 ml of 1% lidocaine in 1:200,000 epinephrine. The local anesthetic was most likely ineffective because of
- (A) acidosis at the site of the injection
- (B) epinephrine-induced limitation of drug diffusion
- (C) insufficient dose
- (D) low ionization of lidocaine
- (E) protein binding of lidocaine
Which of the following is the best initial treatment of anaphylaxis that occurs during general anesthesia?
- (A) Diphenhydramine
- (B) Dopamine
- (C) Epinephrine
- (D) Hydrocortisone
- (E) Ranitidine
An increased initial dose and a decreased maintenance dose of pancuronium are required in patients with
- (A) advanced age
- (B) burns
- (C) cirrhosis
- (D) chronic renal failure
- (E) fever
A 30-year-old woman has an abrupt change from sinus to nodal rhythm with unchanged heart rate on ECG during induction of halothane anesthesia. Which of the following is the most likely result of this change?
- (A) Decreased jugular venous pulsation
- (B) Decreased mean arterial pressure
- (C) Decreased systemic vascular resistance
- (D) Increased cardiac output
- (E) Increased pulse pressure
Inhalation induction of anesthesia is more rapid in a 6-month-old infant than in an adult because infants have
- (A) greater ratio of alveolar ventilation to functional residual capacity
- (B) greater ratio of blood volume to body weight
- (C) greater solubility of anesthetic in blood
- (D) lower anesthetic requirement
- (E) lower distribution of cardiac output to vessel-rich organs
Meperidine has a more rapid onset of action than morphine following intravenous injection because of its
- (A) lesser ionization
- (B) greater lipid solubility
- (C) lesser protein binding
- (D) smaller volume of distribution
- (E) slower rate of hepatic clearance
A 20-year-old man with a history of substance abuse is undergoing preoperative evaluation. Which of the following findings suggests current use of cocaine?
- (A) Absence of deep tendon reflexes
- (B) Bradycardia
- (C) Hypertension
- (D) Hypothermia
- (E) Pinpoint pupils
Compared with similar use in adults, routine use of succinylcholine in children is hazardous because of the increased risk for which of the following?
- (A) Anaphylactoid reaction
- (B) Phase II blockade
- (C) Pseudocholinesterase deficiency
- (D) Pulmonary aspiration
- (E) Undiagnosed myopathy
If administered prior to induction of anesthesia, which of the following drugs is most likely to cause tachycardia?
- (A) Fentanyl
- (B) Meperidine
- (C) Midazolam
- (D) Morphine
- (E) Sufentanil
A 72-year-old woman with stable angina is undergoing bowel resection. Anesthesia is induced with etomidate. Five minutes after starting isoflurane 1% in nitrous oxide 50%, her blood pressure decreases from 110/84 to 70/40 mmHg. The most likely cause is
- (A) coronary steal produced by isoflurane
- (B) direct myocardial depression produced by isoflurane
- (C) vasodilation produced by isoflurane
- (D) adrenocortical suppression produced by etomidate
- (E) myocardial depression produced by etomidate
A patient with jaundice who has a minimally elevated SGOT (AST), markedly elevated alkaline phosphatase, and normal prothrombin time is to receive a muscle relaxant. Which of the following is most likely in this patient?
- (A) Decreased intubating dose of pancuronium
- (B) Increased intubating dose of atracurium
- (C) Prolonged duration of succinylcholine effect
- (D) Prolonged duration of vecuronium effect
- (E) Shortened duration of d-tubocurarine effect
Compared with an induction dose of thiopental (4 mg/kg), an induction dose of propofol (2.5 mg/kg) produces
- (A) better maintenance of cerebral perfusion pressure
- (B) greater inhibition of glucocorticoid production
- (C) higher incidence of myoclonus
- (D) less severe hypotension
- (E) less severe respiratory depression
In a patient with chronic renal failure, which of the following statements concerning muscle relaxants is true?
- (A) Duration of action of vecuronium is prolonged
- (B) The elimination half-life of atracurium is tripled
- (C) Reversal with neostigmine is con train dicated
- (D) The onset of action of mivacurium is delayed
- (E) Succinylcholine is contraindicated
Dantrolene
- (A) antagonizes the effect of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants
- (B) produces clinically detectable muscle weakness when administered intravenously prior to anesthesia
- (C) is indicated for neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- (D) may cause hepatic failure when used prophylactically before anesthesia
- (E) has increased effectiveness when combined with calcium entry blockers
Ketamine decreases
- (A) bronchomotor tone
- (B) intracranial pressure
- (C) intraocular pressure
- (D) salivation
- (E) seizure threshold
Succinylcholine can be administered safely to a patient with
- (A) amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- (B) cerebral palsy
- (C) a pelvic crush injury sustained two weeks ago
- (D) a 20% body surface area burn sustained 10 days ago
- (E) hemiparesis one month after a cerebrovascular accident
Anesthesia is induced with halothane in a 3-year-old girl. Sixty seconds after administration of succinylcholine 1 mg/kg intravenously, heart rate decreases rapidly from 120 to 60 bpm. The most likely cause is
- (A) acute hyperkalemia
- (B) failure to pretreat with a nondepolarizing relaxant
- (C) halothane overdose
- (D) muscarinic activity
- (E) sympathetic ganglionic blockade
Trimethaphan causes each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) cerebral vasodilation
- (B) urinary retention
- (C) pupillary cycloplegia
- (D) histamine release
- (E) potentiation of succinylcholine block
After termination of cardiopulmonary bypass, a patient who is chronically digitalized receives digoxin 0.5 mg in error. An ECG shows sinus bradycardia with intermittent sinus arrest; blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg. Which of the following drugs is contraiindicated in this patient?
- (A) Atropine
- (B) Calcium chloride
- (C) Ephedrine
- (D) Magnesium sulfate
- (E) Phenylephrine
A 15-kg, 3-year-old child is anesthetized for an inguinal hernia repair with halothane and nitrous oxide. The trachea is intubated after administration of succinylcholine 30 mg. At the conclusion of the 45-minute procedure, the child is not breathing; a peripheral nerve twitch monitor indicates no response to a train-of-four stimulus. Further investigation is most likely to show
- (A) abnormal response to nondepolarizing muscle relaxants
- (B) a low dibucaine number
- (C) a low plasma cholinesterase concentration
- (D) an underlying myopathy
- (E) a positive halothane-caffeine contracture test
A 95-kg, 65-year-old woman receives sevoflurane and pancuronium during a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Three minutes after administration of neostigmine 5 mg and atropine 1.2 mg, the twitch height returns to normal. Spontaneous tidal volume is 500 ml when the endotracheal tube is removed. In the PACU she reports dyspnea and appears distressed. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the respiratory distress?
- (A) Atelectasis
- (B) Cholinergic crisis
- (C) Pain
- (D) Residual enflurane
- (E) Residual muscle paralysis
In a patient taking a beta-adrenergic blocker, the drug most likely to produce atrioventricular junctional block is
- (A) diltiazem
- (B) fentanyl
- (C) halothane
- (D) nifedipine
- (E) verapamil
Which of the following is associated with the application of a transdermal fentanyl patch?
- (A) Achievement of a peak plasma level within one hour
- (B) Continued uptake after patch removal
- (C) Dose-independent plasma clearance
- (D) Tachyphylaxis when used for cancer pain
- (E) Naloxone-resistant toxicity
A 69-year-old man is confused and agitated one hour after preoperative intramuscular administration of scopolamine for awake fiberoptic laryngoscopy. SpO2 measured by pulse oximetry is 97%. Which of the following drugs is most appropriate for treatment of the change in mental status?
- (A) Fentanyl
- (B) Flumazenil
- (C) Midazolam
- (D) Neostigmine
- (E) Physostigmine
Epinephrine is less effective in prolonging epidural anesthesia with bupivacaine than epidural anesthesia with lidocaine because
- (A) peak bupivacaine concentrations are decreased less than peak lidocaine concentrations
- (B) the acidic pH of epinephrine decreases the concentration of the nonionized bupivacaine
- (C) bupivacaine produces more vasoconstriction than lidocaine
- (D) the duration of action of bupivacaine is independent of local blood flow
- (E) bupivacaine antagonizes the vasoconstrictor activity of epinephrine
Intravenous administration of mannitol during a craniotomy
- (A) decreases intracranial pressure relative to dosage
- (B) hastens excretion of pancuronium
- (C) induces metabolic alkalosis
- (D) produces a sustained increase in intravascular volume
- (E) requires an intact blood-brain barrier to decrease brain water
Fentanyl-induced bradycardia is
- (A) independent of the speed of injection
- (B) independent of dose
- (C) caused by direct inhibition of adrenal catecholamine release
- (D) caused by vagal stimulation
- (E) caused by direct SA node depression
Which of the following statements concerning the pharmacokinetics of local anesthetics is true?
- (A) Decreased molecular weight is associated with decreased incidence of allergic reactions
- (B) Decreased protein binding is associated with decreased systemic toxicity
- (C) Increased ionization is associated with increased placental transfer
- (D) Increased lipid solubility is associated with faster onset
- (E) Presence of an ester linkage is associated with increased duration of action
Which of the following is the most likely cause of the rapid onset of local anesthesia when sodium bicarbonate is added to lidocaine?
- (A) Decreased extracellular calcium ion concentration
- (B) Increased extracellular pH
- (C) Increased intracellular pH
- (D) Increased ionized lidocaine diffusion
- (E) Increased nonionized lidocaine concentration
The induction dose of thiopental should be decreased in each of the following situations EXCEPT
- (A) age greater than 70 years
- (B) cardiogenic shock
- (C) decreased hepatic blood flow
- (D) hypoalbuminemia
- (E) hypothyroidism
The speed of induction of anesthesia with an inhalational agent is increased by
- (A) decreased cardiac output
- (B) decreased minute ventilation
- (C) increased functional residual capacity
- (D) right-to-left intracardiac shunt
- (E) use of a more soluble agent
Which of the following statements concerning the volume of distribution of a drug is true?
- (A) It is equal to the sum of the volumes of the tissue spaces into which it diffuses
- (B) It is equal to the volume to which it is distributed outside the plasma volume
- (C) It is unaltered by the amount bound to red blood cells and plasma proteins
- (D) It depends on elimination from plasma
- (E) It relates the total amount of the drug in the body to the plasma concentration
In the diagram, point "X" represents a patient with severe left ventricular dysfunction. The points labeled 1, 2, and 3 each represent the results of a different therapeutic intervention. Which of the following represents the most likely intervention at each point?
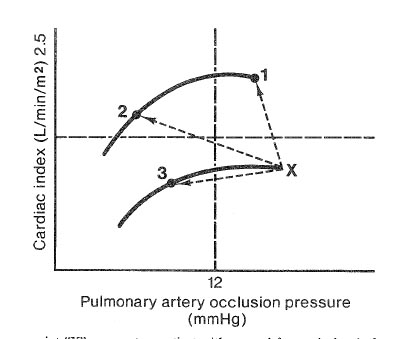
- (A) 1-Dopamine, 2-Furosemide, 3-Nitroprusside
- (B) 1-Dopamine, 2-Nitroprusside, 3-Furosemide
- (C) 1-Furosemide, 2-Dopamine, 3-Nitroprusside
- (D) 1-Nitroprusside, 2-Dopamine, 3-Furosemide
- (E) 1-Nitroprusside, 2-Furosemide, 3-Dopamine
A 68-year-old woman who is receiving urokinase for deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary emboli requires emergency laparotomy for a bleeding gastric ulcer. Which of the following agents is most appropriate to reverse the effects of urokinase?
- (A) Cryoprecipitate
- (B) Factor VIII concentrate
- (C) Fresh frozen plasma
- (D) Platelets
- (E) Vitamin K
Which of the following statements concerning the cardiovascular effects of intravenous bupivacaine is true?
- (A) Intralipid is effective in treating bupivacaine-induced ventricular arrhythmias
- (B) Cardiovascular toxicity is decreased during pregnancy
- (C) Cardiovascular toxicity occurs at lower blood levels than central nervous system toxicity
- (D) Systemic vascular resistance is unchanged
- (E) The rate of impulse conduction through the heart is increased
Which of the following chemotherapeutic drugs is a cause of pulmonary fibrosis?
- (A) Bleomycin
- (B) Cisplatin
- (C) Cyclosporine
- (D) Daunorubicin
- (E) Vincristine
Which of the following statements concerning the metabolism of atracurium is true?
- (A) It is related to cardiac output
- (B) It is decreased by hyperthermia
- (C) It is unaffected by increasing age
- (D) It is decreased by low plasma cholinesterase activity
- (E) It is decreased in renal failure
Each of the following is an adverse effect of ritodrine used for suppression of labor EXCEPT
- (A) dysrhythmias
- (B) hyperglycemia
- (C) hyperkalemia
- (D) hypotension
- (E) pulmonary edema
Which of the following muscle relaxants in an ED95 dose would have the longest duration of action in a patient with renal failure?
- (A) Atracurium
- (B) Metocurine
- (C) Pancuronium
- (D) d-Tubocurarine
- (E) Vecuronium
Which of the following statements concerning hyperkalemia after succinylcholine administration to a patient with a spinal cord injury is true?
- (A) It is unlikely to occur if the lesion is located below T6
- (B) It is unlikely to occur within 24 hours of the injury
- (C) It is unlikely to occur more than 60 days after the initial injury
- (D) It is prevented by pretreatment with small doses of a nondepolarizing agent
- (E) It is decreased in magnitude by pretreatment with calcium chloride
Which of the following is an effect of clonidine?
- (A) Agitation
- (B) Salivation
- (C) Tachycardia
- (D) Tachypnea
- (E) Vasodilation
In patients with renal failure, which of the following muscle relaxants has the most prolonged elimination half-life?
- (A) Atracurium
- (B) Pancuronium
- (C) Succinylcholine
- (D) d-Tubocurarine
- (E) Vecuronium
Which of the following laboratory studies is the best indicator of reversal of the effects of warfarin?
- (A) Activated clotting time
- (B) Activated partial thromboplastin time
- (C) Bleeding time
- (D) Plasma fibrinogen concentration
- (E) Prothrombin time
A 32-year-old patient with end-stage renal failure has irreversible neuromuscular blockade two hours after tracheal intubation with a muscle relaxant. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Atracurium
- (B) Doxacurium
- (C) Mivacurium
- (D) Pancuronium
- (E) Vecuronium
Metoclopramide acts to
- (A) block dopamine receptors
- (B) decrease gastric acid production
- (C) decrease lower esophageal sphincter tone
- (D) delay gastric emptying
- (E) facilitate central cholinergic stimulation
Which of the following statements concerning the effects of glycopyrrolate is true?
- (A) It decreases gastric pH
- (B) It causes bronchoconstriction
- (C) It decreases lower esophageal sphincter tone
- (D) It does not prevent succinylcholine-induced bradycardia
- (E) It causes a central anticholinergic syndrome
Compared with thiopental, methohexital is characterized by
- (A) better absorption after rectal administration
- (B) greater protein binding
- (C) greater hepatic clearance
- (D) larger volume of distribution
- (E) more complete biotransformation
Which of the following is the most likely effect of intramuscular ketamine used for induction of anesthesia in a 2-year-old child undergoing elective surgery?
- (A) Bronchoconstriction
- (B) Decreased heart rate
- (C) Decreased intracranial pressure
- (D) Increased salivation
- (E) Respiratory depression
Intrathecally administered opioids exert their analgesic effects primarily in the
- (A) brain stem
- (B) fourth ventricle
- (C) spinal nerve roots
- (D) spinothalamic tracts
- (E) substantia gelatinosa
During an otherwise uneventful nitrous oxide-sevoflurane anesthetic in a spontaneously breathing patient, 85% nitrous oxide is accidently administered, resulting in a PO2 of 48 mmHg. Which of the following would be expected?
- (A) Tachycardia
- (B) Sweating
- (C) Tachypnea
- (D) Hyperactive EEG
- (E) None of the above
A patient with metastatic carcinoma and chronic renal failure has tremors, fasciculations, mydriasis, and hyperreflexia after several days of therapy with high doses of meperidine for analgesia. Which of the following is most likely to occur if the meperidine is continued?
- (A) Disappearance of the symptoms as tolerance to meperidine develops
- (B) Pinpoint constriction of pupils
- (C) Progressive hypothermia
- (D) Progressive sedation from meperidine toxicity
- (E) Seizures from normeperidine toxicity
Each of the following improves coagulation in patients with uremia EXCEPT
- (A) conjugated estrogens
- (B) desmopressin
- (C) dialysis
- (D) epsilon-aminocaproic acid
- (E) platelet transfusion
At the end of an anesthetic in which a nondepolarizing muscle relaxant was administered, the least number of receptors are blocked
- (A) after administration of neostigmine 5 mg and glycopyrrolate 1 mg
- (B) if the tetanus is sustained at 30 Hz
- (C) if the patient can sustain head lift for 5 sec
- (D) when the ratio of twitch height T1:T4 is 0.8
- (E) when tidal volume is normal
Preoperative evaluation shows a serum sodium concentration of 140 mEq/L, serum chloride concentration of 90 mEq/L, PaCO2 of 46 mmHg, and arterial pH of 7.50. These findings are most indicative of prior treatment with
- (A) acetazolamide
- (B) enalapril
- (C) furosemide
- (D) mannitol
- (E) spironolactone
Pancuronium blocks the bradycardic effect of fentanyl by a direct effect on
- (A) beta-adrenergic receptors
- (B) cardiac muscarinic receptors
- (C) carotid baroreceptors
- (D) central vagal nuclei
- (E) sympathetic ganglia
A 19-year-old woman has severe nausea and vomiting following laparoscopy. After intramuscular administration of prochlorperazine 10 mg, she has muscle spasms in the face, neck, and tongue. Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
- (A) Baclofen
- (B) Diphenhydramine
- (C) Epinephrine
- (D) Hydrocortisone
- (E) Naloxone
A 70-kg, 20-year-old athlete receives nitrous oxide and oxygen, thiopental, and fentanyl 1.25 mg (25 ml) during a knee reconstruction procedure lasting three hours. Postoperatively, he does not awaken or resume spontaneous breathing for three hours. The most likely explanation for the prolonged effect of fentanyl is
- (A) dose-dependent elimination half-life
- (B) genetically slow biotransformation
- (C) large volume of distribution
- (D) presence of an active metabolite in high concentration
- (E) time required for hepatic elimination
When used with morphine for premedication, which of the following drugs is most likely to cause sedation?
- (A) Atropine
- (B) Cephalothin
- (C) Clonidine
- (D) Metoclopramide
- (E) Ranitidine
The drug that causes dose-dependent EEG evidence of both central nervous system excitation and depression is
- (A) lidocaine
- (B) halothane
- (C) thiopental
- (D) nitrous oxide
- (E) midazolam
Which of the following is the most reliable indicator of antagonism of nondepolarizing neuromuscular block sufficient for airway protection?
- (A) Clinically assessed ulnar nerve train-of-four ratio of 0.75
- (B) Peak negative pressure of 25 cmH2O
- (C) End-tidal PC02 of 40 mmHg during spontaneous ventilation
- (D) Sustained head lift for 5 seconds
- (E) Vital capacity of 15 ml/kg
In an unpremedicated, spontaneously breathing patient, an alveolar halothane concentration of 0.74% in oxygen is consistently associated with
- (A) absence of overt response to skin incision
- (B) constricted pupils
- (C) flaccidity of abdominal muscles
- (D) normal glomerular filtration rate
- (E) normal myocardial contractility
Which of the following statements concerning pipecuronium is true?
- (A) It has a faster onset than pancuronium
- (B) It increases systemic vascular resistance
- (C) It induces tachycardia
- (D) It is eliminated by the kidney
- (E) It induces histamine release
Each of the following would be expected after preoperative oral administration of clonidine EXCEPT
- (A) bradycardia in the absence of surgical stimulation
- (B) decreased requirement for inhalational anesthetics
- (C) decreased requirement for opioid anesthetics
- (D) decreased response to exogenous epinephrine
- (E) sedation
A 16-year-old girl is receiving isoflurane, nitrous oxide, oxygen, and pancuronium for insertion of a Harrington rod. In order to perform a "wake-up test" the muscle relaxant was antagonized with neostigmine 2.5 mg and atropine 1 mg. The patient abruptly moved all extremities and was given thiopental 100 mg and succinylcholine 100 mg rapidly. Forty-five minutes later no twitch could be elicited with a nerve stimulator. The most likely explanation is
- (A) a dibucaine number of 20
- (B) incomplete antagonism of pancuronium
- (C) prolongation of the action of succinylcholine by neostigmine
- (D) spinal cord damage caused by the abrupt arousal
- (E) synergism between succinylcholine and pancuronium
The alveolar concentrations of anesthetics increase more rapidly in children than in adults because of a greater
- (A) blood volume (per kg body mass)
- (B) cardiac index
- (C) MAC
- (D) ratio of alveolar ventilation to functional residual capacity
- (E) tidal volume (per kg body mass)
A single dose of etomidate for induction of anesthesia will cause
- (A) adrenal cortical suppression
- (B) decreased skeletal muscle tone
- (C) hypotension
- (D) increased airway reactivity
- (E) tachycardia
Which of the following would be most likely to increase the duration of seizures during electroconvulsive therapy using a barbiturate and succinyleholine for general anesthesia?
- (A) Administration of atropine prior to therapy
- (B) Changing to a benzodiazepine for induction
- (C) Changing to etomidate for induction
- (D) Adding phenytoin to preoperative medications
- (E) Decreasing the dose of barbiturate used for induction
The use of droperidol as a preanesthetic medication has been associated with each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) acute anxiety
- (B) anterograde amnesia
- (C) hypotension
- (D) extrapyramidal signs
- (E) catalepsy
A 70-kg man has stable 80% neuromuscular block induced with d-tubocurarine. Compared with neostigmine 3 mg, antagonism with edrophonium 70 mg will
- (A) be of shorter duration
- (B) be of slower onset
- (C) be less reliable
- (D) produce less change in heart rate
- (E) require more anticholinergic
A 55-kg, 70-year-old woman with mild chronic renal failure is unresponsive 20 hours after an uneventful coronary artery bypass grafting procedure. Anesthetic drugs included fentanyl 3000 mcg, diazepam 35 mg, and pancuronium 20 mg. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- (A) Administration of edrophonium
- (B) Administration of flumazenil
- (C) Administration of naloxone
- (D) CT scan of the head
- (E) Measurement of core body temperature
A healthy, but obese, 110-kg woman is scheduled for gastric stapling. Compared with that required at her ideal weight, the dose of thiopental required for anesthetic induction would likely be increased because of changes in
- (A) blood volume
- (B) muscle mass
- (C) circulation time
- (D) body fat
- (E) metabolic rate
Which of the following drugs is LEAST likely to cross the placenta?
- (A) Lidocaine
- (B) Meperidine
- (C) Midazolam
- (D) Thiopental
- (E) Vecuronium
The best premedication regimen for a known active narcotic addict would include
- (A) secobarbital
- (B) diazepam
- (C) nalbuphine
- (D) morphine
- (E) droperidol
Which of the following is a known effect of propofol?
- (A) Decreased amplitude of somatosensory evoked potentials
- (B) Induction of malignant hyperthermia
- (C) Inhibition of cytochrome P450
- (D) Initiation of porphyria
- (E) Suppression of adrenocortical function
Which of the following statements concerning a patient who has been receiving nitroprusside for several days is true?
- (A) Biotransformation of cyanide requires a sulfur donor
- (B) Formation of methemoglobin increases cyanide toxicity
- (C) Increased serum thiocyanate concentrations are innocuous
- (D) Mixed venous P02 decreases as cyanide toxicity develops
- (E) Serum thiocyanate concentrations reflect the degree of cyanide toxicity
Which of the following statements concerning ketorolac is true?
- (A) It binds to opioid receptors
- (B) It causes dose-related thrombocytopenia
- (C) It decreases heart rate during isoflurane anesthesia
- (D) It is eliminated unchanged in urine
- (E) It reversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase
Bupivacaine is more likely than lidocaine to cause refractory cardiac arrest because bupivacaine
- (A) has a lower rate of plasma clearance
- (B) has a secondary blocking effect on cardiac beta,-adrenergic receptors
- (C) dissociates more slowly from sodium channels in cardiac muscle
- (D) inhibits spontaneous phase 4 depolarization in pacemaker cells
- (E) preferentially blocks calcium channels in Purkinje fibers
A 62-year-old man is scheduled for coronary artery bypass grafting. During induction of anesthesia with fentanyl, high peak inspiratory pressures occur with manual ventilation, and peripheral oxygen saturation decreases from 100% to 94%. The most appropriate management is administration of
- (A) albuterol
- (B) isoflurane
- (C) midazolam
- (D) nitroglycerin
- (E) succinylcholine
Delirium produced by high doses of atropine can be reversed by intravenous injection of
- (A) diphenhydramine
- (B) flumazenil
- (C) naloxone
- (D) neostigmine
- (E) physostigmine
To predict the requirement for isoflurane in milliliters of vapor per minute during closed circuit anesthesia, each of the following is necessary EXCEPT
- (A) cardiac output
- (B) oxygen consumption
- (C) MAC of isoflurane
- (D) duration of administration
- (E) blood-gas partition coefficient
Which of the following is an effect of nitrous oxide?
- (A) Decreased pulmonary vascular resistance
- (B) Depression of uterine contractility
- (C) Inhibition of methionine synthetase
- (D) Stimulation of lymphocyte chemotaxis
- (E) Stimulation of myocardial contractility
Each of the following statements about muscle rigidity induced by opioids is true EXCEPT:
- (A) The degree of rigidity is related to the rate of opioid administration
- (B) It is more apparent during the administration of nitrous oxide
- (C) Muscles of the trunk are affected more than muscles of the extremities
- (D) It results from a direct effect of the opioid on skeletal muscles
- (E) It can be produced by large doses of morphine
A 76-year-old patient is restless and hallucinating in the preoperative holding area. He received morphine 5 mg and scopolamine 0.4 mg intramuscularly as premedication and is now breathing oxygen 2 L/min through nasal prongs. SpO2 is 98%. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- (A) Administration of naloxone
- (B) Administration of physostigmine
- (C) Induction of general anesthesia
- (D) Determination of serum electrolyte concentrations
- (E) CT scan of the head
Nonsteroidal analgesics such as aspirin decrease pain by
- (A) decreasing axonal transmission of pain stimuli through a local anesthetic mechanism
- (B) directly competing with substance P for receptor occupancy
- (C) inhibiting enzymatic breakdown of met-enkephalin
- (D) inhibiting production of prostaglandin E2
- (E) potentiating the action of endorphin in the substantia gelantinosa of the spinal cord
A 70-kg 78-year-old man undergoing small-bowel resection during anesthesia with isoflurane in oxygen becomes hypotensive and develops frothy pink sputum in the endotracheal tube. Heart rate is 50 bpm, blood pressure is 75/60 mmHg, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure is 22 mmHg, and cardiac output is 1.7 L/min. The most appropriate initial step in management is administration of which of the following?
- (A) Albumin
- (B) Digoxin
- (C) Dopamine
- (D) Esmolol
- (E) Nitroglycerin
A patient with end-stage renal disease has prolonged ventilatory depression after administration of morphine. The most likely cause is increased
- (A) serum concentration of morphine-6-glucuronide
- (B) elimination half-life of morphine
- (C) opioid receptors
- (D) receptor affinity
- (E) volume of distribution
Which of the following statements concerning diazepam is true?
- (A) Absorption is more predictable after intramuscular administration than after oral administration
- (B) It produces a shift to the left of the carbon dioxide ventilatory response curve
- (C) Rebound drowsiness is caused by a metabolite
- (D) The degree of CNS depression is independent of serum albumin concentration
- (E) The extent of amnesia is proportional to the degree of sedation
A patient has palpitations, flushing, and light-headedness after gingival injection of a local anesthetic. This reaction is most likely caused by
- (A) epinephrine in the local anesthetic
- (B) local anesthetic allergy
- (C) para-aminobenzoic acid allergy
- (D) methylparaben reaction
- (E) vasovagal reaction
When the inspired gas is changed from air to 20% oxygen and 80% nitrous oxide, PaO2 increases because
- (A) increased pulmonary artery pressure perfuses alveoli that previously enhanced dead space
- (B) nitrous oxide stimulates the respiratory center
- (C) rapid absorption of nitrous oxide increases alveolar oxygen concentration
- (D) replacement of nitrogen by nitrous oxide expands atelectatic alveoli
- (E) respiratory depression from nitrous oxide shifts the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve
Which of the following drugs has the shortest elimination half-life?
- (A) Diazepam
- (B) Flumazenil
- (C) Flumazepam
- (D) Lorazepam
- (E) Midazolam
Compared with morphine 5 mg administered epidurally at T12, morphine 5 mg administered intravenously is associated with
- (A) greater incidence of urinary retention
- (B) less intense analgesia
- (C) less nausea and vomiting
- (D) longer duration of analgesia
- (E) longer time to maximum analgesia
Following protamine administration, profound pulmonary hypertension is most likely initiated by release of
- (A) epinephrine
- (B) histamine
- (C) leukotriene
- (D) norepinephrine
- (E) thromboxane
Desflurane is delivered using a vaporizer that contains internal heaters because
- (A) heat decreases the drug's viscosity
- (B) heat reduces thermal loss in the patient
- (C) heat increases the drug's oil-gas partition coefficient
- (D) heat prevents fluctuations of vapor pressure
- (E) it does not vaporize adequately at room temperature
Mivacurium-induced neuromuscular blockade is prolonged for the greatest period of time in patients who have which of the following conditions?
- (A) Ethanol-induced hepatitis
- (B) Hemiplegia
- (C) Pseudocholinesterase deficiency
- (D) Renal insufficiency
- (E) Thermal burns
Each of the following is consistent with exposure to organophosphates EXCEPT
- (A) bronchodilation
- (B) muscle weakness
- (C) salivation
- (D) sweating
- (E) urinary retention
Which of the following muscle relaxants has a prolonged duration of action in a patient who is homozygous for atypical plasma cholinesterase?
- (A) Atracurium
- (B) Doxacurium
- (C) Mivacurium
- (D) Pipecuronium
- (E) Vecuronium
A 23-year-old man who is receiving his first anesthetic has not resumed spontaneous ventilation two hours after receiving succinylcholine. The train-of-four monitor shows no twitch response. Which of the following is the most likely cholinesterase genotype in this patient?
- (A) Atypical : atypical
- (B) Fluoride-resistant : fluoride-resistant
- (C) Fluoride-resistant : silent
- (D) Normal : normal
- (E) Normal : silent
Compared with epidural administration of hydrophilic opioids, epidural administration of lipophilic opioids is associated with
- (A) earlier onset of pruritus
- (B) greater motor block when combined with local anesthetics
- (C) higher incidence of delayed respiratory depression
- (D) lesser sensitivity to reversal of analgesia by naloxone
- (E) slower onset of analgesia
In a 35-year-old patient, which of the following is associated with an increased duration of clinical narcosis following infusion of a total dose of 10 mg/kg thiopental over three hours?
- (A) Alcoholism in remission
- (B) Asthma
- (C) Fever
- (D) Obesity
- (E) Use of appetite suppressants
Which of the following is the most likely adverse effect of prolonged intravenous administration of nitroglycerin?
- (A) Cyanmethemoglobinemia
- (B) Hemolysis
- (C) Methemoglobinemia
- (D) Neutropenia
- (E) Thrombocytopenia
Which of the following findings would be considered normal in the EEG of an adult?
- (A) Decreased frequency during induction with halogenated anesthetics
- (B) Decreased frequency in frontal areas with administration of nitrous oxide 50%
- (C) Dominance of beta rhythm at 20 to 30 Hz during the awake relaxed state
- (D) Electrical silence with administration of isoflurane 2.5 MAC
- (E) The presence of burst-suppression during natural sleep
Which of the following increases during infusion of epinephrine?
- (A) Glycogen synthesis
- (B) Intracellular glucose concentration
- (C) Intracellular potassium concentration
- (D) Lipogenesis
- (E) Protein synthesis
After administration of a single dose of vecuronium, function returns last to which of the following muscles?
- (A) Adductor pollicis
- (B) Diaphragm
- (C) Laryngeal muscles
- (D) Orbicularis oculi
- (E) Rectus abdominis
Phase II neuromuscular block is characterized by
- (A) depressed twitch height, sustained tetanus, post-tetanic potentiation
- (B) depressed twitch height, tetanic fade, post-tetanic potentiation
- (C) depressed twitch height, tetanic fade, no post-tetanic potentiation
- (D) normal twitch height, tetanic fade, post-tetanic potentiation
- (E) normal twitch height, tetanic fade, no post-tetanic potentiation
Each of the following is an effect of rapid infusion of mannitol EXCEPT
- (A) depletion of electrolytes
- (B) impaired platelet adhesiveness
- (C) increased intracranial pressure
- (D) increased intravascular fluid volume
- (E) increased renal blood flow
Which of the following is a characteristic of phase II neuromuscular block?
- (A) It is diagnosed by the intravenous administration of calcium
- (B) It is potentiated by edrophonium
- (C) It produces nondepolarizing train-of-four characteristics
- (D) It requires evaluation for pseudocholinesterase deficiency
- (E) It requires less succinylcholine than a phase I block
A newly developed volatile anesthetic has a MAC of 10% in oxygen for adults. Which of the following statements concerning this anesthetic is true?
- (A) The expected MAC of this drug in combination with 60% nitrous oxide is 7.5%
- (B) The dose of this drug required to anesthetize a patient with acute amphetamine intoxication is less than the dose required for a normal patient
- (C) The potency of this drug is 25% of a drug with a MAC of 2.5%
- (D) The dose of this drug required to suppress the hormonal response to surgical incision is less than the MAC value
- (E) The MAC of this drug is decreased by metabolic alkalosis
Each of the following decreases hepatic blood flow EXCEPT
- (A) isoflurane anesthesia
- (B) spinal anesthesia
- (C) hypercarbia
- (D) mechanical ventilation
- (E) positive end-expiratory pressure
Which of the following muscle relaxants is most likely to result in histamine release following administration of a bolus dose sufficient to facilitate rapid endotracheal intubation?
- (A) Atracurium
- (B) Pancuronium
- (C) Succinylcholine
- (D) Rocuronium
- (E) Vecuronium
A patient develops jaundice one week after undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy during halothane anesthesia. Laboratory studies show an increased serum alkaline phosphatase concentration, a mildly increased serum aspartate aminotransferase concentration, and a markedly increased conjugated bilirubin fraction. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- (A) Biliary obstruction
- (B) Gilbert's disease
- (C) Halothane-associated hepatitis
- (D) Hematoma resorption
- (E) Infectious hepatitis
The following hemodynamic values are obtained two hours after coronary artery bypass surgery: Cardiac index 1.7 L/min/m2; Pulm Art. Occ. Pressure 22 mmHg; MAP 60 mmHg; Urine volume 0.2 ml/kg/hr. The most appropriate management is
- (A) dopamine infusion
- (B) nitroprusside infusion
- (C) norepinephrine infusion
- (D) volume expansion
- (E) observation without intervention
Each of the following is a recognized complication during a transurethral resection for which glycine is used as an irrigant EXCEPT
- (A) disseminated intravascular coagulopathy
- (B) hemolysis
- (C) hyperammonemia
- (D) shoulder pain
- (E) transient blindness
Compared with dopamine, dobutamine
- (A) is more useful in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors because it depends on the release of norepinephrine for its effect
- (B) is more useful in patients in right heart failure because it does not increase pulmonary vascular resistance
- (C) has no positive chronotropic response
- (D) induces diuresis without increasing cardiac output
- (E) in doses greater than 10 mcg/kg/min increases systemic vascular resistance more than similar doses of dopamine
An obese patient and a lean patient receive halothane for the same duration and at the same inspired tension. Postoperatively, the obese patient would demonstrate
- (A) higher serum creatinine concentration
- (B) higher serum fluoride concentration
- (C) lower eosinophil count
- (D) lower serum alkaline phosphate activity
- (E) lower serum bromide concentration
Which of the following is an effect of metoclopramide?
- (A) Decreased lower esophageal sphincter tone
- (B) Decreased MAC for enflurane
- (C) Extrapyramidal signs
- (D) Increased gastric pH
- (E) Relief of intestinal obstruction
In a patient who is receiving nitroglycerin intravenously after a coronary artery operation, peripheral oxygen saturation is 85% and PaO2 is 200 mmHg. The most appropriate management is administration of
- (A) exchange transfusion
- (B) hydroxocobalamin
- (C) methylene blue
- (D) pure oxygen at 3 atmospheres
- (E) thiocyanate
A 64-year-old, 70-kg woman treated with lithium for manic-depressive psychosis is given methohexital 90 mg and succinylcholine 35 mg intravenously for electroconvulsive therapy. Ten minutes later she remains sedated and the peripheral nerve stimulator shows a decreased twitch response. The most likely explanation is
- (A) cerebral hypoxia
- (B) postictal depression
- (C) relative overdose of methohexital
- (D) unrecognized atypical pseudocholinesterase
- (E) residual lithium effects
A patient has tonic movements of the head and neck, nystagmus, and slurred speech after receiving metoclopramide for nausea after nitrous oxide-opioid anesthesia. The most appropriate pharmacologic treatment is
- (A) diphenhydramine
- (B) midazolam
- (C) naloxone
- (D) phenytoin
- (E) physostigmine
A 72-year-old patient who takes levodopa and carbidopa is undergoing colon resection. Metoclopramide is administered preoperatively and anesthesia is maintained with proposal, fentanyl, and nitrous oxide, with vecuronium for muscle relaxation. Fifteen minutes after reversal of muscle relaxation with neostigmine and atropine and tracheal extubation, the patient has dyspnea and muscular rigidity. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
- (A) Central anticholinergic syndrome
- (B) Fentanyl-induced rigidity
- (C) Inhibition of methionine synthetase by nitrous oxide
- (D) Metoclopramide-induced dopamine antagonism
- (E) Peripheral conversion of levodopa to dopamine
Which of the following opioids is vagolytic?
- (A) Morphine
- (B) Meperidine
- (C) Sufentanil
- (D) Nalbuphine
- (E) Alfentanil
A 75-year-old woman with significant carotid artery stenosis is scheduled for general anesthesia for repair of a fractured hip. Which of the following is the greatest disadvantage of using propofol as an induction agent in this patient?
- (A) Decreased arterial blood pressure
- (B) Pain during intravenous injection
- (C) Prolonged apnea after induction
- (D) Prolonged awakening
- (E) Prolonged elimination half-life
Each of the following conditions is associated with upregulation of the acetylcholine receptor at the neuromuscular junction EXCEPT
- (A) burn injuries
- (B) myasthenia gravis
- (C) prolonged bed rest
- (D) prolonged use of neuromuscular relaxants
- (E) upper motor neuron injury
Each of the following conditions causes resistance to nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockade EXCEPT
- (A) chronic severe infections
- (B) major burns
- (C) myotonia congenita
- (D) prolonged immobilization
- (E) upper motor neuron injury
The highest serum fluoride levels are seen following the administration of which of the following volatile anesthetics?
- (A) Desflurane
- (B) Enflurane
- (C) Halothane
- (D) Isoflurane
- (E) Sevoflurane
A patient is anesthetized using an inhaled anesthetic with a blood/gas partition coefficient of 13.0. Recovery time depends primarily on
- (A) oil/gas solubility of the drug
- (B) cardiac output
- (C) tidal volume
- (D) duration of administration
- (E) MAC of the drug
For 30 minutes, a patient has been receiving oxygen 2 L, nitrous oxide 2 L, and halothane from an agent-specific vaporizer set at 1%. A mass spectrometer sampling gas from the patient's airway shows an end-tidal halothane concentration of 0.7%. The most likely explanation for this difference is
- (A) hyperventilation
- (B) low cardiac output
- (C) the second-gas effect
- (D) tissue solubility of halothane
- (E) vaporizer temperature less than 19°C
A 73-year-old woman with a preoperative serum creatinine concentration of 2.1 mg/dl develops oliguria during enflurane anesthesia. Urine sodium concentration is 10 mEq/L and urine osmolality is 450 mOsm/L. The most likely cause of these findings is
- (A) acute renal failure
- (B) chronic renal insufficiency
- (C) decreased renal perfusion
- (D) fluoride nephrotoxicity
- (E) intraoperative administration of furosemide
Compared with lidocaine, bupivacaine is more likely to cause dysrhythmias because it
- (A) enhances potassium-hydrogen ion exchange
- (B) is less soluble in lipids
- (C) produces more prolonged block of sodium channels
- (D) sensitizes the myocardium to catecholamines
- (E) sustains calcium channels open
Which of the following is a sign of cyanide toxicity during nitroprusside therapy?
- (A) Decreased SpO2
- (B) Increased PaCO2
- (C) Increased arteriovenous oxygen tension difference
- (D) Increased mixed venous pH
- (E) Increased mixed venous PO2
In treating arterial hypertension in a patient with a head injury, the agent LEAST likely to increase intracranial pressure is
- (A) hydralazine
- (B) nitroprusside
- (C) nitroglycerin
- (D) trimethaphan
- (E) halothane
The short clinical duration of action of a single dose of fentanyl is a result of its
- (A) small volume of distribution
- (B) large volume of distribution
- (C) low lipid solubility
- (D) rapid redistribution
- (E) short elimination half-life
Which of the following conditions is a contraindication to the use of succinylcholine?
- (A) Burns of 50% body surface area occurring 12 hours ago
- (B) Cirrhosis
- (C) Myotonic dystrophy
- (D) Seizure disorder
- (E) Spinal cord transection within the past six hours
Which of the following decreases the clearance of atracurium?
- (A) Administration of cimetidine
- (B) Cholinesterase deficiency
- (C) Hepatic insufficiency
- (D) Hypothermia
- (E) Renal insufficiency
A previously healthy 28-year-old woman scheduled for laparoscopic tubal ligation becomes, agitated and refuses to undergo the procedure after being brought to the operating room. This behavior most likely resulted from preoperative administration of
- (A) droperidol
- (B) cimetidine
- (C) atropine
- (D) meperidine
- (E) midazolam
Which of the following statements concerning flumazenil is true?
- (A) Hepatic clearance is low
- (B) It binds irreversibly with the benzodiazepine receptor
- (C) It causes hypertension and tachycardia
- (D) It has a shorter duration of action than midazolam
- (E) It reverses opioid-induced respiratory depression
When antagonizing neuromuscular block produced by pancuronium, the combination of simultaneously administered anticholinergic and anticholinesterase drugs that is most likely to produce bradycardia is
- (A) glycopyrrolate and pyridostigmine
- (B) atropine and edrophonium
- (C) glycopyrrolate and edrophonium
- (D) atropine and neostigmine
- (E) glycopyrrolate and neostigmine
The figure describes the uptake of nitrous oxide 75% by individual tissue groups (VRG = vessel-rich group, MG = muscle group, FG = fat group) and their sum (total uptake, TU). Which set of labels accurately describes the curves?
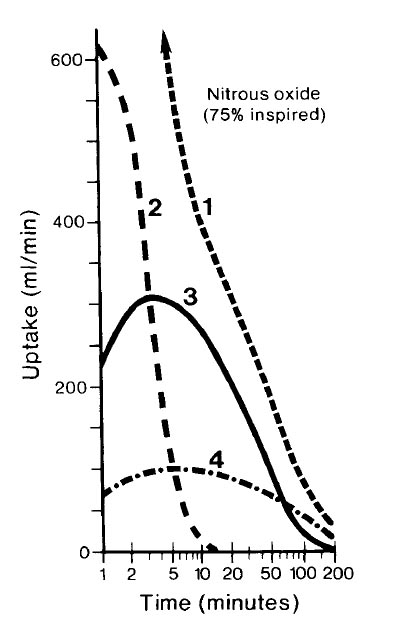
- (A) 1- MG, 2- FG, 3- VRG, 4- TU
- (B) 1- VRG, 2- MG, 3- FG, 4- TU
- (C) 1- FG, 2- MG, 3- TU, 4- VRG
- (D) 1- TU, 2- FG, 3- MG, 4- VRG
- (E) 1- TU, 2- VRG, 3- MG, 4- FG
The duration of action of an induction dose of thiopental is determined primarily by its
- (A) rate of elimination
- (B) rate of metabolism
- (C) redistribution from brain to fat
- (D) redistribution from brain to muscle
- (E) hepatic extraction
The twitch responses shown are from a healthy 80-kg patient anesthetized with fentanyl and nitrous oxide. Relaxant drugs X and Y are most likely
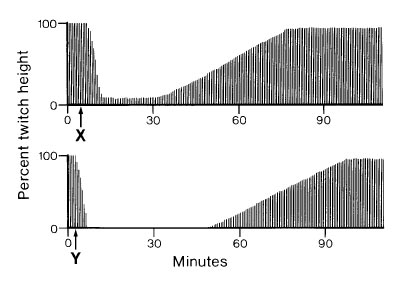
- (A) X: atracurium 30 mg, Y: vecuronium 4 mg
- (B) X: atracurium 30 mg, Y: vecuronium 8 mg
- (C) X: pancuronium 4 mg, Y: pancuronium 8 mg
- (D) X: vecuronium 4 mg, Y: atracurium 30 mg
- (E) X: vecuronium 4 mg, Y: pancuronium 8 mg
Neostigmine administered intravenously without atropine can produce each of the following EXCEPT
- (A) arousal
- (B) bradycardia
- (C) bronchoconstriction
- (D) increased gastric motility
- (E) increased urinary bladder tone
In a patient taking a beta-adrenergic blocker, the drug most likely to produce atrioventricular junctional block is
- (A) diltiazem
- (B) fentanyl
- (C) halothane
- (D) nifedipine
- (E) verapamil
Ten days after sustaining burns over 40% of his body surface area, a patient requires greater than expected doses of vecuronium for adequate relaxation of skeletal muscle. The primary cause is increased
- (A) plasma protein binding of d-tubocurarine
- (B) metabolism of d-tubocurarine
- (C) number of acetylcholine receptors
- (D) renal clearance of d-tubocurarine
- (E) blood flow to skeletal muscle
A complication of terbutaline therapy to terminate premature labor is
- (A) bronchoconstriction
- (B) hypoglycemia
- (C) fetal bradycardia
- (D) closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus
- (E) pulmonary edema
Following enflurane anesthesia, serum free fluoride concentration is most likely to be increased in association with long-term use of
- (A) diazepam
- (B) ethanol
- (C) isoniazid
- (D) phenobarbital
- (E) phenytoin
The EKG rhythm shown developed during cholecystectomy in a 62-year-old man who had a myocardial infarction and is taking atenolol. The drug of choice for treating this arrhythmia is
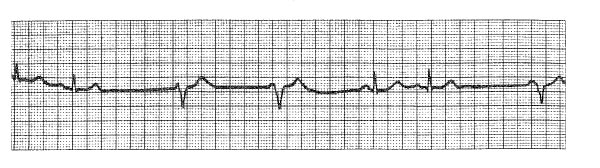
- (A) atropine
- (B) bretylium
- (C) isoproterenol
- (D) lidocaine
- (E) procainamide
A 64-year-old man with diabetes mellitus well controlled with NPH insulin undergoes lower extremity revascularization. Following administration of protamine 10 mg, the patient has facial flushing and blood pressure of 60/30 mmHg. The most appropriate initial step in management is administration of which of the following drugs?
- (A) Diphenhydramine
- (B) Epinephrine
- (C) Hydrocortisone
- (D) Norepinephrine
- (E) Phenylephrine
When succinylcholine is administered intravenously to infants, intragastric pressure
- (A) is usually unchanged
- (B) increases to a peak of 30 cmH20 within two minutes
- (C) increases because of abdominal muscle fasciculations
- (D) increases because of an acetylcholine-like effect on the vagus nerve
- (E) peaks and subsides within five minutes
Of the following, the most reliable criterion for adequate clinical reversal of neuromuscular blockade is
- (A) return of twitch height to 90% of normal
- (B) peak inspiratory force of -20 cmH20
- (C) T4:T1 ratio of 0.75 for train of four
- (D) normal tidal volume
- (E) disappearance of post-tetanic facilitation
The five curves shown represent the uptake of enflurane, desflurane, halothane, isoflurane, and nitrous oxide. Which uptake curve best depicts desflurane?

- (A) Curve A
- (B) Curve B
- (C) Curve C
- (D) Curve D
- (E) Curve E
Desflurane at a stable alveolar concentration of 7%
- (A) causes bradycardia
- (B) decreases cerebrovascular resistance
- (C) degrades in soda lime
- (D) increases systemic vascular resistance
- (E) stimulates the respiratory centers
Compared with halothane, desflurane has which of the following characteristics?
- (A) Greater potency
- (B) A higher boiling point
- (C) Increased blood solubility
- (D) Less airway irritability
- (E) Less biodegradation
Metoclopramide
- (A) decreases gastric acid secretion
- (B) decreases gastroesophageal sphincter tone
- (C) is contraindicated in patients with Parkinson's disease
- (D) is most effective when administered in combination with atropine
- (E) requires an intact vagus nerve for gastrointestinal effects
Halothane
- (A) has no effect on reflex hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
- (B) protects the myocardium from beta-adrenergic stimulation
- (C) has a direct, negative chronotropic effect on the sinoatrial node
- (D) metabolites decrease renal concentrating ability
- (E) is unsafe for use with epinephrine-containing local anesthetics
Inhibition of labor by terbutaline causes each of the following maternal side effects EXCEPT
- (A) hyperkalemia
- (B) hypotension
- (C) ventricular dysrhythmias
- (D) hyperglycemia
- (E) pulmonary edema
The action of dantrolene on skeletal muscle
- (A) occurs within the neuromuscular junction
- (B) alters electrical properties of the muscle membrane
- (C) does not result in muscle relaxation
- (D) decreases myoplasmic calcium concentration
- (E) results from competitive inhibition of caffeine
A 70-year-old man who has just undergone an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair under halothane anesthesia develops hypertension, dyspnea, and cyanosis shortly after awakening in the recovery room. Administration of furosemide 20 mg intravenously improves the cyanosis within 10 minutes. This immediate effect of furosemide is best explained by
- (A) inotropic effect from electrolyte shifts
- (B) decreased preload through diuresis
- (C) increased peripheral venous capacitance
- (D) decreased pulmonary vascular resistance
- (E) increased coronary blood flow
Prolonged respiratory depression following administration of morphine is more likely in patients with chronic renal faillure than in patients with normal kidney function because of
- (A) decreased biotransformation
- (B) decreased protein binding
- (C) decreased volume of distribution
- (D) delayed excretion of morphine metabolites
- (E) the effect of acidosis on morphine ionization
The decreased duration of action of an intravenous dose of fentanyl compared with an intravenous dose of morphine is best explained by
- (A) greater lipid solubility
- (B) increased hepatic metabolism
- (C) less protein binding
- (D) shorter elimination half-life
- (E) smaller volume of distribution
Each of the following is an effect of acute preoperative oral administration of clonidine EXCEPT
- (A) sedation
- (B) respiratory depression
- (C) decreased intraoperative plasma catecholamine concentrations
- (D) decreased MAC of inhalational anesthetics
- (E) decreased perioperative opioid requirement
At equipotent doses, which of the following opioids is most likely to migrate cephalad in cerebrospinal fluid after epidural administration?
- (A) Fentanyl
- (B) Hydromorphone
- (C) Meperidine
- (D) Morphine
- (E) Sufentanil
Each of the following is a characteristic of prostaglandin E1 (alprostadil) pharmacology in an infant EXCEPT:
- (A) It is effective in the treatment of large left-to-right shunts
- (B) It is a cause of apnea
- (C) It is a potent vasodilator
- (D) It prevents closure of the ductus arteriosus
- (E) It is metabolized rapidly
A 24-year-old woman requires anesthesia for emergency repair of open fractures of the tibia and fibula. She used cocaine two hours ago. Blood pressure is 170/110 mmHg. Each of the following is useful in managing the hypertension EXCEPT
- (A) hydralazine
- (B) labetalol
- (C) nitroprusside
- (D) phentolamine
- (E) propranolol
Which of the following drugs administered to a parturient eliminates fetal heart rate variability?
- (A) Atropine
- (B) Ephedrine
- (C) Hydralazine
- (D) Magnesium sulfate
- (E) Terbutaline
Intraocular pressure is
- (A) decreased by glycopyrrolate
- (B) increased by hyperventilation
- (C) decreased by halothane
- (D) increased by nondepolarizing muscle relaxants
- (E) increased by phenylephrine eye drops
Local anesthetics block nerve conduction by
- (A) closing calcium channels
- (B) decreasing intracellular calcium concentration
- (C) decreasing potassium conductance
- (D) causing extrusion of intracellular potassium
- (E) inhibiting cellular influx of sodium
Compared with morphine, a single epidural administration of fentanyl is associated with
- (A) delayed onset of analgesia
- (B) increased incidence of pruritus
- (C) increased incidence of respiratory depression
- (D) longer duration of action
- (E) more restricted segmental spread
Which of the following is most responsible for the duration of action of local anesthetics?
- (A) Concentration
- (B) Metabolism
- (C) Molecular weight
- (D) Tissue protein binding
- (E) Volume injected
Which of the following is an effect of ketorolac administered after vaginal hysterectomy?
- (A) Euphoria
- (B) Prolonged prothrombin time
- (C) Respiratory depression
- (D) Suppression of inflammation
- (E) Thrombocytopenia
Spontaneously breathing enflurane at 1 MAC causes increased
- (A) airway resistance
- (B) diaphragm function
- (C) carbon dioxide production
- (D) intercostal muscle function
- (E) physiologic dead space
A patient has severe hypotension, bronchospasm, and edema of the upper airway after injection of radiocontrast medium during cerebral angiography. The most appropriate immediate treatment is administration of
- (A) diphenhydramine
- (B) epinephrine
- (C) methylprednisolone
- (D) phenylephrine
- (E) ranitidine
Cyanide toxicity from nitroprusside is unlikely in patients with renal dysfunction because
- (A) renal excretion of thiosulfate is decreased
- (B) metabolic acidosis inactivates cyanide
- (C) anemia inhibits breakdown of nitroprusside by oxyhemoglobin
- (D) thiocyanate is formed in the liver
- (E) the dose of nitroprusside necessary to lower blood pressure is greatly decreased
Compared with other volatile inhalation anesthetics, desflurane has which of the following characteristics?
- (A) Equipotency to isoflurane
- (B) Greater extent of biotransformation than enflurane
- (C) Less airway irritation than halothane
- (D) Lower blood gas solubility coefficient than enflurane
- (E) Lower vapor pressure than isoflurane
Administration of succinylcholine 1 mg/kg to a pregnant woman rarely causes fetal neuromuscular blockade. Which characteristic of succinylcholine best explains this phenomenon?
- (A) High protein binding
- (B) Ionization
- (C) Lack of passive placental diffusion
- (D) Lipid solubility
- (E) Metabolism in the fetal liver
Which of the following is a potentially beneficial effect of ketamine used for induction of anesthesia?
- (A) Analgesia
- (B) Attenuation of respiratory response to carbon dioxide
- (C) Decreased cerebral metabolic rate
- (D) Increased stroke volume in patients with hemorrhagic shock
- (E) Preservation of laryngeal reflexes