58 questions match your search.
Each of the following improves coagulation in patients with uremia EXCEPT
- (A) conjugated estrogens
- (B) desmopressin
- (C) dialysis
- (D) epsilon-aminocaproic acid
- (E) platelet transfusion
Each of the following is consistent with exposure to organophosphates EXCEPT
- (A) bronchodilation
- (B) muscle weakness
- (C) salivation
- (D) sweating
- (E) urinary retention
Which of the following drugs administered to a parturient eliminates fetal heart rate variability?
- (A) Atropine
- (B) Ephedrine
- (C) Hydralazine
- (D) Magnesium sulfate
- (E) Terbutaline
A previously healthy 28-year-old woman scheduled for laparoscopic tubal ligation becomes, agitated and refuses to undergo the procedure after being brought to the operating room. This behavior most likely resulted from preoperative administration of
- (A) droperidol
- (B) cimetidine
- (C) atropine
- (D) meperidine
- (E) midazolam
A 70-year-old man who has just undergone an abdominal aortic aneurysm repair under halothane anesthesia develops hypertension, dyspnea, and cyanosis shortly after awakening in the recovery room. Administration of furosemide 20 mg intravenously improves the cyanosis within 10 minutes. This immediate effect of furosemide is best explained by
- (A) inotropic effect from electrolyte shifts
- (B) decreased preload through diuresis
- (C) increased peripheral venous capacitance
- (D) decreased pulmonary vascular resistance
- (E) increased coronary blood flow
The effect of neomycin at the neuromuscular junction is
- (A) decreased by depolarizing relaxants
- (B) partially reversed by calcium
- (C) potentiated by anticholinesterases
- (D) prevented by pretreatment with magnesium
- (E) primarily prejunctional
A patient has tonic movements of the head and neck, nystagmus, and slurred speech after receiving metoclopramide for nausea after nitrous oxide-opioid anesthesia. The most appropriate pharmacologic treatment is
- (A) diphenhydramine
- (B) midazolam
- (C) naloxone
- (D) phenytoin
- (E) physostigmine
After termination of cardiopulmonary bypass, a patient who is chronically digitalized receives digoxin 0.5 mg in error. An ECG shows sinus bradycardia with intermittent sinus arrest; blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg. Which of the following drugs is contraiindicated in this patient?
- (A) Atropine
- (B) Calcium chloride
- (C) Ephedrine
- (D) Magnesium sulfate
- (E) Phenylephrine
Inhibition of labor by terbutaline causes each of the following maternal side effects EXCEPT
- (A) hyperkalemia
- (B) hypotension
- (C) ventricular dysrhythmias
- (D) hyperglycemia
- (E) pulmonary edema
Dantrolene
- (A) antagonizes the effect of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants
- (B) produces clinically detectable muscle weakness when administered intravenously prior to anesthesia
- (C) is indicated for neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- (D) may cause hepatic failure when used prophylactically before anesthesia
- (E) has increased effectiveness when combined with calcium entry blockers
Which of the following statements concerning neuroleptic malignant syndrome is true?
- (A) It does not respond to dantrolene therapy
- (B) It is inherited as an autosomal trait
- (C) It is not triggered by succinylcholine
- (D) It occurs after long-term use of L-dopa
- (E) The halothane-caffeine contracture test is negative in susceptible patients
Following protamine administration, profound pulmonary hypertension is most likely initiated by release of
- (A) epinephrine
- (B) histamine
- (C) leukotriene
- (D) norepinephrine
- (E) thromboxane
Each of the following is a characteristic of prostaglandin E1 (alprostadil) pharmacology in an infant EXCEPT:
- (A) It is effective in the treatment of large left-to-right shunts
- (B) It is a cause of apnea
- (C) It is a potent vasodilator
- (D) It prevents closure of the ductus arteriosus
- (E) It is metabolized rapidly
A 64-year-old man with diabetes mellitus well controlled with NPH insulin undergoes lower extremity revascularization. Following administration of protamine 10 mg, the patient has facial flushing and blood pressure of 60/30 mmHg. The most appropriate initial step in management is administration of which of the following drugs?
- (A) Diphenhydramine
- (B) Epinephrine
- (C) Hydrocortisone
- (D) Norepinephrine
- (E) Phenylephrine
A 15-kg, 3-year-old child is anesthetized for an inguinal hernia repair with halothane and nitrous oxide. The trachea is intubated after administration of succinylcholine 30 mg. At the conclusion of the 45-minute procedure, the child is not breathing; a peripheral nerve twitch monitor indicates no response to a train-of-four stimulus. Further investigation is most likely to show
- (A) abnormal response to nondepolarizing muscle relaxants
- (B) a low dibucaine number
- (C) a low plasma cholinesterase concentration
- (D) an underlying myopathy
- (E) a positive halothane-caffeine contracture test
Each of the following is an effect of rapid infusion of mannitol EXCEPT
- (A) depletion of electrolytes
- (B) impaired platelet adhesiveness
- (C) increased intracranial pressure
- (D) increased intravascular fluid volume
- (E) increased renal blood flow
A 65-year-old patient receiving long-term clonidine therapy fails to take it one day before surgery. This would most likely
- (A) be beneficial, since clonidine decreases cardiac output
- (B) be of no consequence due to the long half-life of clonidine
- (C) produce a lower anesthetic requirement than if the drug had been continued
- (D) produce rebound hypertension
- (E) result in seizure activity
Each of the following is an effect of acute preoperative oral administration of clonidine EXCEPT
- (A) sedation
- (B) respiratory depression
- (C) decreased intraoperative plasma catecholamine concentrations
- (D) decreased MAC of inhalational anesthetics
- (E) decreased perioperative opioid requirement
Administration of succinylcholine 1 mg/kg to a pregnant woman rarely causes fetal neuromuscular blockade. Which characteristic of succinylcholine best explains this phenomenon?
- (A) High protein binding
- (B) Ionization
- (C) Lack of passive placental diffusion
- (D) Lipid solubility
- (E) Metabolism in the fetal liver
A complication of terbutaline therapy to terminate premature labor is
- (A) bronchoconstriction
- (B) hypoglycemia
- (C) fetal bradycardia
- (D) closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus
- (E) pulmonary edema
Each of the following would be expected after preoperative oral administration of clonidine EXCEPT
- (A) bradycardia in the absence of surgical stimulation
- (B) decreased requirement for inhalational anesthetics
- (C) decreased requirement for opioid anesthetics
- (D) decreased response to exogenous epinephrine
- (E) sedation
A 35-year-old woman with a grade III subarachnoid hemorrhage is undergoing clipping of a middle cerebral artery aneurysm 48 hours after initial hemorrhage. Which of the following drugs used to induce hypotension is LEAST likely to affect intracranial pressure?
- (A) Esmolol
- (B) Hydralazine
- (C) Isoflurane
- (D) Nitroglycerin
- (E) Sodium nitroprusside
Anesthesia is induced with halothane in a 3-year-old girl. Sixty seconds after administration of succinylcholine 1 mg/kg intravenously, heart rate decreases rapidly from 120 to 60 bpm. The most likely cause is
- (A) acute hyperkalemia
- (B) failure to pretreat with a nondepolarizing relaxant
- (C) halothane overdose
- (D) muscarinic activity
- (E) sympathetic ganglionic blockade
A 76-year-old patient is restless and hallucinating in the preoperative holding area. He received morphine 5 mg and scopolamine 0.4 mg intramuscularly as premedication and is now breathing oxygen 2 L/min through nasal prongs. SpO2 is 98%. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- (A) Administration of naloxone
- (B) Administration of physostigmine
- (C) Induction of general anesthesia
- (D) Determination of serum electrolyte concentrations
- (E) CT scan of the head
When succinylcholine is administered intravenously to infants, intragastric pressure
- (A) is usually unchanged
- (B) increases to a peak of 30 cmH20 within two minutes
- (C) increases because of abdominal muscle fasciculations
- (D) increases because of an acetylcholine-like effect on the vagus nerve
- (E) peaks and subsides within five minutes
Each of the following is an adverse effect of ritodrine used for suppression of labor EXCEPT
- (A) dysrhythmias
- (B) hyperglycemia
- (C) hyperkalemia
- (D) hypotension
- (E) pulmonary edema
Which of the following drugs is LEAST likely to cross the placenta?
- (A) Lidocaine
- (B) Meperidine
- (C) Midazolam
- (D) Thiopental
- (E) Vecuronium
The concentration of bupivacaine is higher in maternal blood than in fetal blood because
- (A) bupivacaine is metabolized in the placenta
- (B) maternal blood has a higher pH
- (C) maternal blood has greater plasma protein binding
- (D) maternal hemoglobin has a higher affinity for bupivacaine
- (E) placental transfer of bupivacaine is limited
Prilocaine is NOT recommended for obstetric regional anesthesia because it
- (A) causes fetal methemoglobinemia
- (B) has a very short duration of action
- (C) is not metabolized by the newborn
- (D) is the most toxic of the amide local anesthetics
- (E) produces a longer motor block than sensory block
During therapy for eclampsia, toxic blood levels of magnesium sulfate can be distinguished from therapeutic levels by the presence of
- (A) diminished knee jerk reflex
- (B) a widened QRS complex on EKG
- (C) fetal tachycardia
- (D) maternal drowsiness
- (E) uterine rigidity
Hyperkalemia in response to the administration of an intubating dose of succinylcholine is associated with each of the following disorders EXCEPT
- (A) poliomyelitis
- (B) multiple sclerosis
- (C) hemiplegia
- (D) acute cervical cord transection
- (E) familial periodic paralysis
Compared with similar use in adults, routine use of succinylcholine in children is hazardous because of the increased risk for which of the following?
- (A) Anaphylactoid reaction
- (B) Phase II blockade
- (C) Pseudocholinesterase deficiency
- (D) Pulmonary aspiration
- (E) Undiagnosed myopathy
A 55-kg, 70-year-old woman with mild chronic renal failure is unresponsive 20 hours after an uneventful coronary artery bypass grafting procedure. Anesthetic drugs included fentanyl 3000 mcg, diazepam 35 mg, and pancuronium 20 mg. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- (A) Administration of edrophonium
- (B) Administration of flumazenil
- (C) Administration of naloxone
- (D) CT scan of the head
- (E) Measurement of core body temperature
The physiologic function most likely to be spared when a local anesthetic differential nerve block is administered is
- (A) sweating
- (B) temperature sensation
- (C) proprioception
- (D) touch sensation
- (E) pain sensation
Which of the following drugs exerts a vasoconstrictor effect by blocking the reuptake of norepinephrine at the neuronal synapse?
- (A) Cocaine
- (B) Dopamine
- (C) Ephedrine
- (D) Metaraminol
- (E) Phenylephrine
The induction dose of thiopental should be decreased in each of the following situations EXCEPT
- (A) age greater than 70 years
- (B) cardiogenic shock
- (C) decreased hepatic blood flow
- (D) hypoalbuminemia
- (E) hypothyroidism
A 64-year-old, 70-kg woman treated with lithium for manic-depressive psychosis is given methohexital 90 mg and succinylcholine 35 mg intravenously for electroconvulsive therapy. Ten minutes later she remains sedated and the peripheral nerve stimulator shows a decreased twitch response. The most likely explanation is
- (A) cerebral hypoxia
- (B) postictal depression
- (C) relative overdose of methohexital
- (D) unrecognized atypical pseudocholinesterase
- (E) residual lithium effects
Metoclopramide
- (A) decreases gastric acid secretion
- (B) decreases gastroesophageal sphincter tone
- (C) is contraindicated in patients with Parkinson's disease
- (D) is most effective when administered in combination with atropine
- (E) requires an intact vagus nerve for gastrointestinal effects
Compared with epidural administration of hydrophilic opioids, epidural administration of lipophilic opioids is associated with
- (A) earlier onset of pruritus
- (B) greater motor block when combined with local anesthetics
- (C) higher incidence of delayed respiratory depression
- (D) lesser sensitivity to reversal of analgesia by naloxone
- (E) slower onset of analgesia
Each of the following is a recognized complication during a transurethral resection for which glycine is used as an irrigant EXCEPT
- (A) disseminated intravascular coagulopathy
- (B) hemolysis
- (C) hyperammonemia
- (D) shoulder pain
- (E) transient blindness
In treating arterial hypertension in a patient with a head injury, the agent LEAST likely to increase intracranial pressure is
- (A) hydralazine
- (B) nitroprusside
- (C) nitroglycerin
- (D) trimethaphan
- (E) halothane
Which of the following would be most likely to increase the duration of seizures during electroconvulsive therapy using a barbiturate and succinyleholine for general anesthesia?
- (A) Administration of atropine prior to therapy
- (B) Changing to a benzodiazepine for induction
- (C) Changing to etomidate for induction
- (D) Adding phenytoin to preoperative medications
- (E) Decreasing the dose of barbiturate used for induction
In the diagram, point "X" represents a patient with severe left ventricular dysfunction. The points labeled 1, 2, and 3 each represent the results of a different therapeutic intervention. Which of the following represents the most likely intervention at each point?
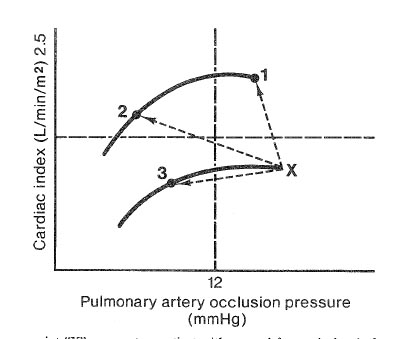
- (A) 1-Dopamine, 2-Furosemide, 3-Nitroprusside
- (B) 1-Dopamine, 2-Nitroprusside, 3-Furosemide
- (C) 1-Furosemide, 2-Dopamine, 3-Nitroprusside
- (D) 1-Nitroprusside, 2-Dopamine, 3-Furosemide
- (E) 1-Nitroprusside, 2-Furosemide, 3-Dopamine
Which of the following is associated with the application of a transdermal fentanyl patch?
- (A) Achievement of a peak plasma level within one hour
- (B) Continued uptake after patch removal
- (C) Dose-independent plasma clearance
- (D) Tachyphylaxis when used for cancer pain
- (E) Naloxone-resistant toxicity
The low fetal/maternal plasma ratio of bupivacaine compared with lidocaine is due to
- (A) fetal tissue binding
- (B) fetal plasma protein binding
- (C) maternal plasma protein binding
- (D) ionization in maternal blood
- (E) ionization in fetal blood
In a patient who is receiving nitroglycerin intravenously after a coronary artery operation, peripheral oxygen saturation is 85% and PaO2 is 200 mmHg. The most appropriate management is administration of
- (A) exchange transfusion
- (B) hydroxocobalamin
- (C) methylene blue
- (D) pure oxygen at 3 atmospheres
- (E) thiocyanate
Inhalation induction of anesthesia is more rapid in a 6-month-old infant than in an adult because infants have
- (A) greater ratio of alveolar ventilation to functional residual capacity
- (B) greater ratio of blood volume to body weight
- (C) greater solubility of anesthetic in blood
- (D) lower anesthetic requirement
- (E) lower distribution of cardiac output to vessel-rich organs
A 23-year-old man who is receiving his first anesthetic has not resumed spontaneous ventilation two hours after receiving succinylcholine. The train-of-four monitor shows no twitch response. Which of the following is the most likely cholinesterase genotype in this patient?
- (A) Atypical : atypical
- (B) Fluoride-resistant : fluoride-resistant
- (C) Fluoride-resistant : silent
- (D) Normal : normal
- (E) Normal : silent
Succinylcholine can be administered safely to a patient with
- (A) amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- (B) cerebral palsy
- (C) a pelvic crush injury sustained two weeks ago
- (D) a 20% body surface area burn sustained 10 days ago
- (E) hemiparesis one month after a cerebrovascular accident
Intravenous administration of mannitol during a craniotomy
- (A) decreases intracranial pressure relative to dosage
- (B) hastens excretion of pancuronium
- (C) induces metabolic alkalosis
- (D) produces a sustained increase in intravascular volume
- (E) requires an intact blood-brain barrier to decrease brain water
One week after sustaining third-degree burns over 40% of his body surface area, a patient requires general anesthesia for debridement and skin grafting. Which of the following responses to neuromuscular blockers is most likely?
- (A) Clinically insignificant increases in serum potassium concentration after administration of succinylcholine 1 mg/kg
- (B) Increased risk of hyperkalemia after administration of succinylcholine 1 mg/kg
- (C) Increased sensitivity to vecuronium
- (D) Laudanosine toxicity after administration of atracurium 0.4 mg/kg
- (E) Normal serum potassium concentration if administration of succinylcholine is preceded by d-tubocurarine 3 mg
Which of the following conditions is a contraindication to the use of succinylcholine?
- (A) Burns of 50% body surface area occurring 12 hours ago
- (B) Cirrhosis
- (C) Myotonic dystrophy
- (D) Seizure disorder
- (E) Spinal cord transection within the past six hours
The following hemodynamic values are obtained two hours after coronary artery bypass surgery: Cardiac index 1.7 L/min/m2; Pulm Art. Occ. Pressure 22 mmHg; MAP 60 mmHg; Urine volume 0.2 ml/kg/hr. The most appropriate management is
- (A) dopamine infusion
- (B) nitroprusside infusion
- (C) norepinephrine infusion
- (D) volume expansion
- (E) observation without intervention
Miosis, incontinence, excess salivation, and convulsions are toxic effects of
- (A) amphetamines
- (B) phenothiazines
- (C) cocaine
- (D) tricyclic antidepressants
- (E) organophosphate insecticides
The alveolar concentrations of anesthetics increase more rapidly in children than in adults because of a greater
- (A) blood volume (per kg body mass)
- (B) cardiac index
- (C) MAC
- (D) ratio of alveolar ventilation to functional residual capacity
- (E) tidal volume (per kg body mass)
Which of the following is an effect of acetazolamide?
- (A) Glucose intolerance
- (B) Increased minute ventilation
- (C) Metabolic alkalosis
- (D) Sinus bradycardia
- (E) Slowed intravenous anesthetic induction
A patient receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy for depression undergoes an emergency cholecystectomy. Which of the following is the best means of providing postoperative analgesia in this patient?
- (A) Epidural analgesia using 0.25% bupivacaine
- (B) Intravenous meperidine
- (C) Epidural analgesia using meperidine
- (D) Epidural analgesia using 1% lidocaine with epinephrine
- (E) Intercostal analgesia using 1% lidocaine with epinephrine
In a patient who is to undergo clipping of a cerebral aneurysm, an advantage of isoflurane over nitroprusside for induction of hypotension is
- (A) better maintenance of cardiac output
- (B) better maintenance of cerebral blood flow
- (C) greater decrease in cerebral oxygen consumption
- (D) greater decrease in afterload
- (E) more rapid titration of systemic blood pressure